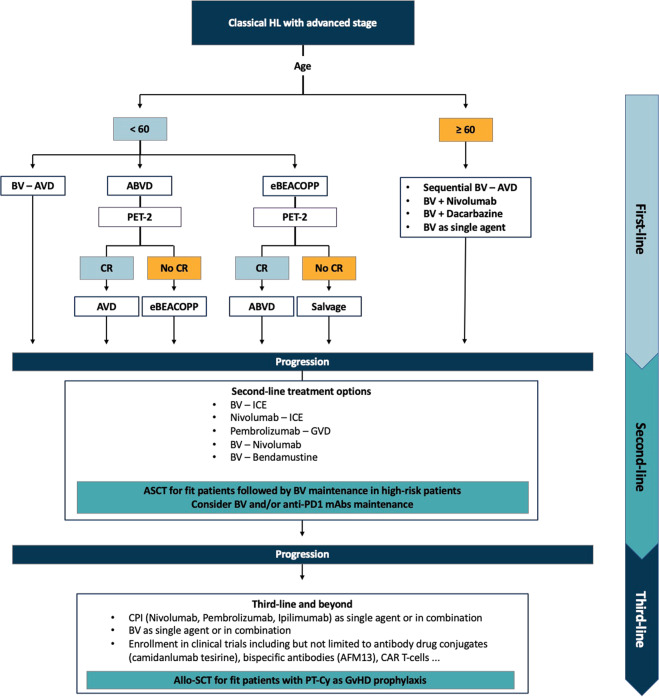
Fig. 1. Suggested treatment algorithm for advanced-stage classical Hodgkin Lymphoma.
In the frontline setting, patients are treated according to age. In patients aged <60 years, the treatment options can be either immunotherapy (BV) combined with AVD or risk-adapted PET-guided approaches using ABVD and/or eBEACOPP. In patients aged >60 years, the intensity of therapies should be adapted to comorbidities. In the relapsed setting, chemoimmunotherapeutic or chemotherapy-free approaches can be used. ASCT is recommended for fit patients followed by BV maintenance for high-risk patients (a shorter duration of BV or the use of anti-PD1 mAbs alone or in combination with BV may be considered). Beyond third-line therapy, immunotherapy can be used as single agent or in combination. Also, patients can be included in clinical trials using novel agents or cellular therapy. Allo-SCT remains the standard of care for fit and responding patients. PT-Cy should be considered as GvDH prophylaxis for all patients undergoing allo-SCT, even in the non-haploidentical settings. HL: Hodgkin Lymphoma; ABVD: Adriamycin, Bleomycin, Vincristine, Dacarbazine; eBEACOPP: bleomycin, etoposide, doxorubicin (aka adriamycin),cyclophosphamide, vincristine (aka oncovin), procarbazine, prednisolone; PET: positron emission tomography; BV: brentuximab vedotin; AVD: Adriamycin, Vincristine, Dacarbazine; GVD: gemcitabine, vinorelbine, liposomal doxorubicin; CR: complete response; ICE: ifosfamide, mesna, carboplatin, etoposide; ASCT: autologous stem cell transplantation; PD1: programmed cell death 1; mAbs: monoclonal antibodies; CPI: checkpoint inhibitors; Allo-SCT: allogeneic stem cell transplantation; PT-Cy: post-transplant cyclophosphamide; GvHD: graft-versus-host disease.