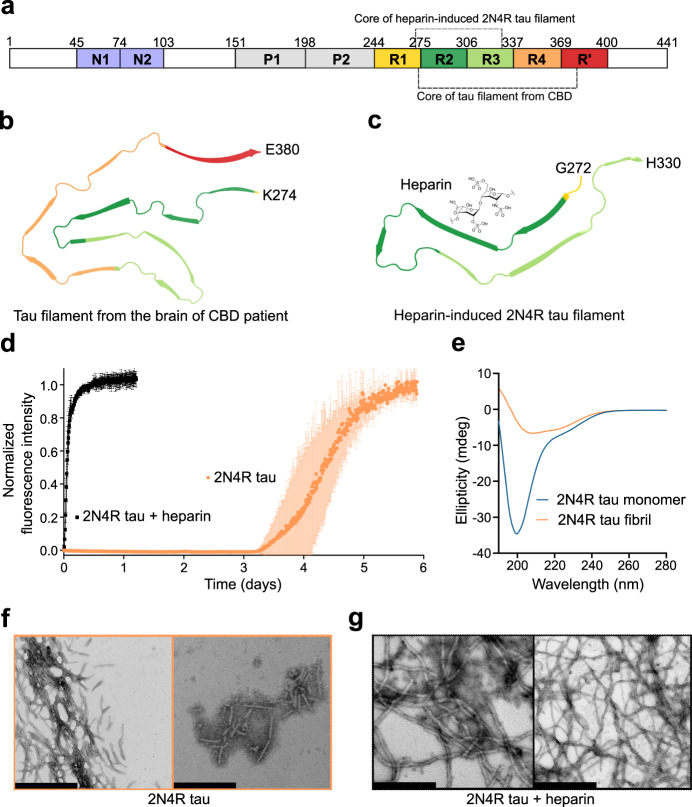
Fig. 1. Amyloid fibrils of tau without co-factors.
a Schematic representation of the domain organization of 2N4R tau. N1 and N2 are two inserts subject to alternative splicing, P1 and P2 mark the proline-rich regions, and R1-R’ are pseudo-repeats that bind to microtubules. Tau fibril cores from CBD-brain and heparin-induced 2N4R fibrils are marked by dashed lines (see also (b, c)). b CryoEM structure of tau filament (type 1) extracted from the brain of a patient with CBD (PDB code: 6TJO). c CryoEM structure of heparin-induced 2N4R tau fibrils (snake form; PDB code: 6QJH). A molecule of heparin is displayed to illustrate that these fibrils are formed in the presence of heparin. d Aggregation kinetics of 25 µM 2N4R tau with (black) and without (orange) heparin. Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation of n = 3 independent samples. e Circular dichroism spectra of 2N4R tau monomer and heparin-free fibrils. f, g Negative-stain electron micrographs of 2N4R fibrils aggregated without heparin (f) or with heparin (g). Scale bar, 500 nm. Similar micrographs have been observed for both 2N4R fibrils aggregated in presence/absence of heparin with ten independently aggregated samples.