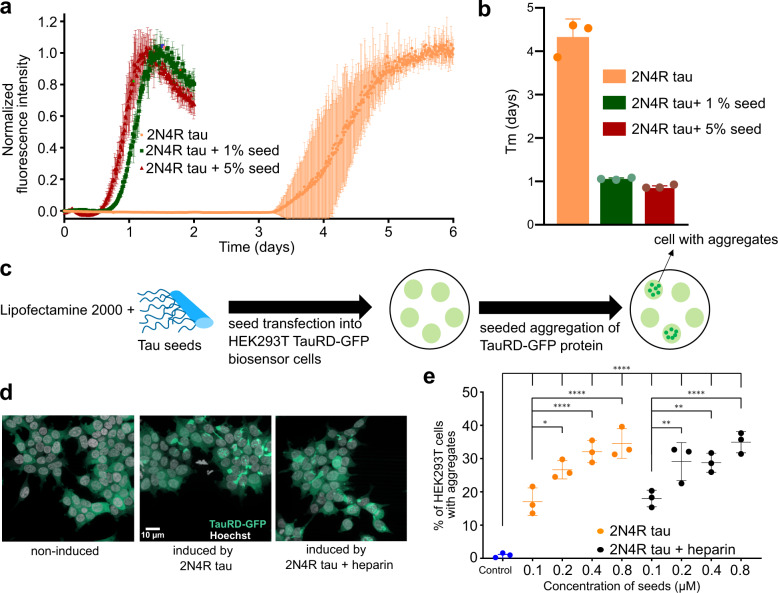
Fig. 5. Seeding activity of heparin-free tau fibrils.
a Aggregation kinetics of 25 µM 2N4R tau in the absence (orange) and presence of 1% (green) and 5% (red) tau seeds generated without heparin. Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation of n = 3 independent samples. b Half-time (Tm) of aggregation of 2N4R tau in the absence (orange) and presence of 1% (green), 5% (red) tau seeds (see (a)). Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation of n = 3 independent samples. c Schematic representation of the process of seeding of tau aggregation in biosensor cells. d TauRD-GFP puncta in HEK293T biosensor cells23, expressing the tau repeat domain carrying the mutations P301L and V337M, induced by 2N4R tau seeds, which were formed either in the absence (left) or presence of heparin (right). The result was reproducible for three independently performed experiments. e Comparison of the efficiency of 2N4R tau seeding in tau biosensor cells. Fibrils were generated by aggregating 2N4R tau in the absence (orange) or presence (black) of heparin. Different concentrations of seeds (0.1–0.8 µM) were used to induce TauRD-GFP puncta. The statistical analysis between the % of HEK293T cells with puncta induced by each concentration of seeds in the absence/presence of heparin was performed by one-way ANOVA analysis. Fibrils of different concentrations were independently transfected n = 3 times. Error bars represent the standard deviation of three independent experiments. Four stars represent p < 0.0001, two stars represents p ≤ 0.0021, one star represents p = 0.0296.