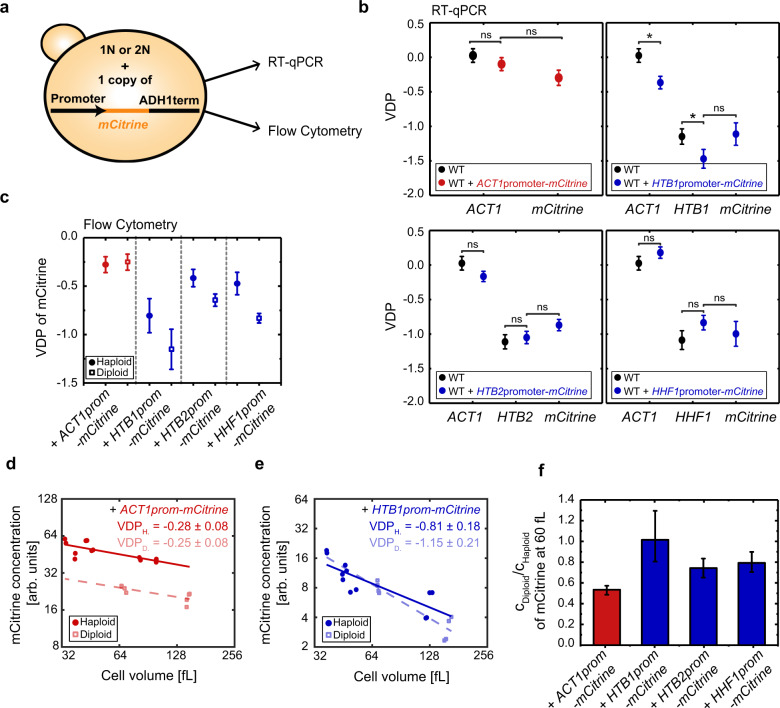
Fig. 3. Histone promoters are sufficient for cell-volume- and ploidy-dependence of transcript concentrations.
a Illustration of haploid (1N) or diploid (2N) strains carrying a single additional copy of a promoter of interest, driving the expression of the fluorescent reporter mCitrine regulated by the ADH1 terminator. RT-qPCR or flow cytometry were used to analyze expression of the fluorescent reporter. b Summary of VDPs determined with RT-qPCR for the genes ACT1, mCitrine, and HTB1, HTB2, or HHF1 for a haploid strain carrying an additional ACT1 promoter (red circles), and haploid strains carrying an additional HTB1, HTB2, or HHF1 promoter (blue circles) in comparison to a wild-type strain (black circles). VDPs were determined as the slope of the linear fit to the double-logarithmic dependence of concentration on cell volume (fit through , , , , , , , , , , biological replicates), with error bars indicating the standard error of the VDPs. Significant VDP deviation between two genes was tested using linear regressions; *, *. c Summary of VDPs determined with flow cytometry for different strains in haploid (filled circles) and diploid (open squares) cells. VDPs were determined as the slope of the linear fit to the double-logarithmic dependence of concentration on cell volume (fit through , , , , , , biological replicates), with error bars indicating the standard error of the VDPs. d, e mCitrine concentration, driven by an additional copy of the ACT1 (d) or HTB1 (e) promoter in haploid (filled circles) and diploid (open squares) cells, shown as a function of cell volume in a double-logarithmic plot. Lines show linear fits to the double-logarithmic data with volume-dependence parameters (VDPs) determined as the slope of the fit, with respective standard error. f Concentration of mCitrine, estimated from the linear fit to the double-logarithmic dependence of concentration on cell volume, in diploid cells compared to the concentration in haploid cells at 60 fL. Error bars indicate the 2.5- and 97.5-percentiles around the median concentration ratio, determined from 10,000 bootstrap samples.