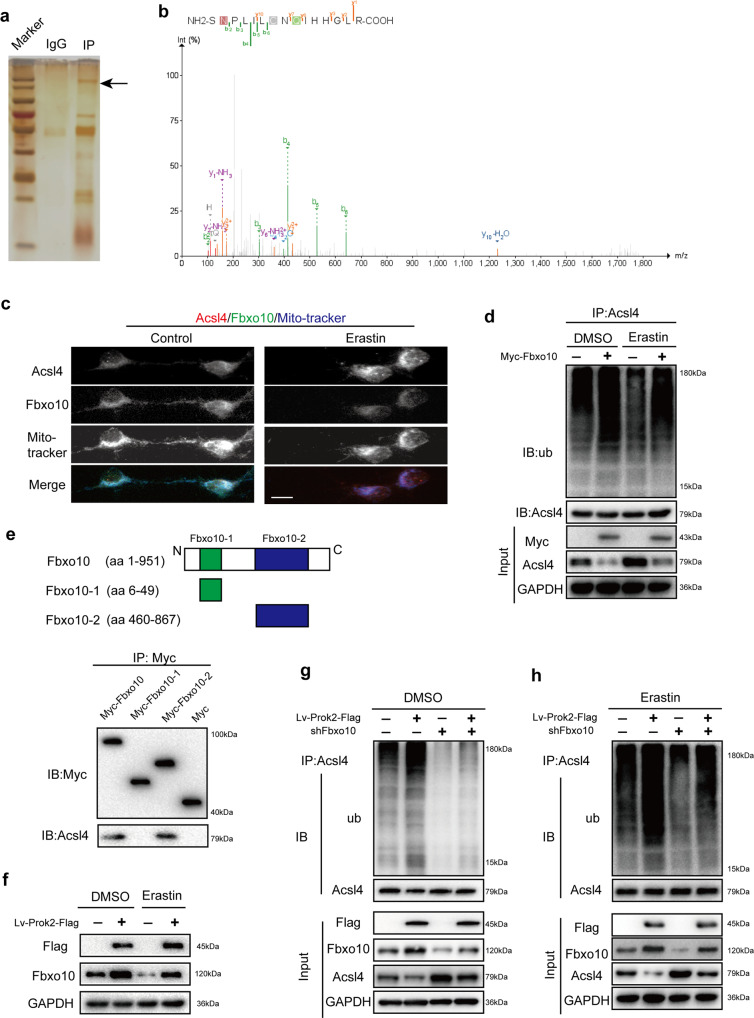
Fig. 5. Fbxo10 is crucial in Prok2-induced Acsl4 ubiquitination.
a Cell lysates obtained from primary cortical neurons are immunoprecipitated with Acsl4 antibody. Silver staining is used to reveal all proteins bound to Acsl4 antibody. Mass spectrometry analysis identified Fbxo10 as the only ubiquitin ligase in the extracted protein from primary cortical neurons. b Mass spectrogram of Fbxo10. c Immunofluorescence staining shows co-localization of Fbxo10 (green), Acsl4 (red) and Mito-tracker (blue) in primary cortical neurons. Scale bar is 10 μm. d IP with Acsl4 followed by western blot with anti-Ub shows that overexpression of Fbxo10 increases ubiquitination of Acsl4 in the presence or absence of Erastin. e Schematic representation of Fbxo10 fusion proteins (upper part). Interaction is detected between Fbxo10 domains (aa 460–867) and Acsl4 (lower part). f Overexpression of Prok2 in primary cortical neurons increases Fbxo10 protein levels in the presence or absence of Erastin. g, h Primary neurons are co-transfected with Lv-Prok2-Flag and Fbxo10 shRNA. Cell lysates are obtained and immunoprecipitated with Acsl4 antibody followed by western blot with anti-Ub. Prok2-induced ubiquitination of Acsl4 is decreased in Fbxo10-knockdown cells both in the presence and absence of Erastin. Acsl4 is used as a control in IP lysates; GAPDH is used as a control in input lysates. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.