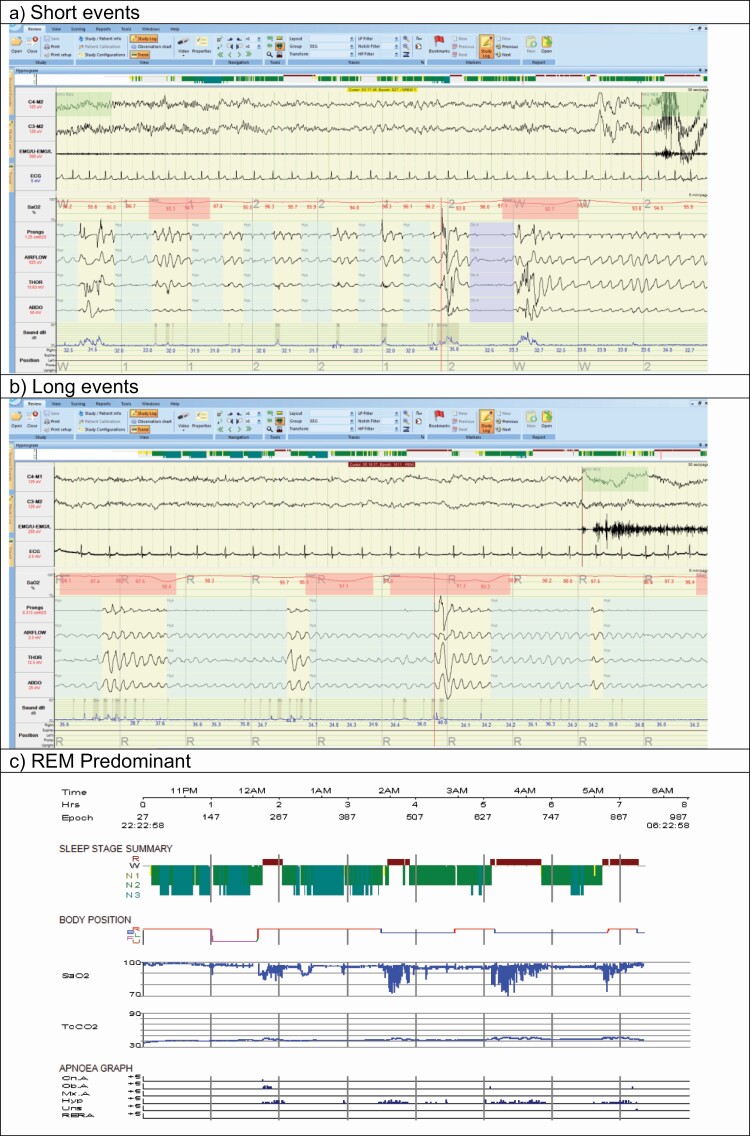
Figure 2.
Examples of different patterns of obstructive respiratory events for people with AHI in the range 20–30 events/hour: (a) Short events (AHI = 21.3 events/hour, Average hypopnea duration 20 seconds, maximum duration 55 seconds), (b) Long events (AHI = 25.6 events/hour: Average hypopnea duration 31 seconds, maximum duration 92 seconds), (c) REM predominant (AHI= 21.5 events/hour: REM AHI = 67.5 events/hour, NREM AHI = 5.5 events/hour). The images show cut-down PSG montage signals (a, b) = EEG, sub-mental EMG and ECG signals at 30 seconds per page and pulse oximeter (SaO2), nasal pressure transducer (prongs), oronasal thermal flow sensor (AIRFLOW), respiratory effort thoracic (THOR), respiratory effort abdominal (ABDO), sound intensity and body position at 5 minutes per page or hypnogram signals (c) = study time (Time), Epoch number (Epoch), Sleep stage summary, body position, pulse oximetry (SaO2), scored Central (Cn. A), Obstructive (Ob. A), Mixed (Mx. A), hypopnea (Hyp), unsure (Uns), and respiratory event-related arousals (RERA). Abbreviations: AHI: apnea-hypopnea index, REM: rapid eye movement, NREM: non-rapid eye movement, PSG: polysomnography.