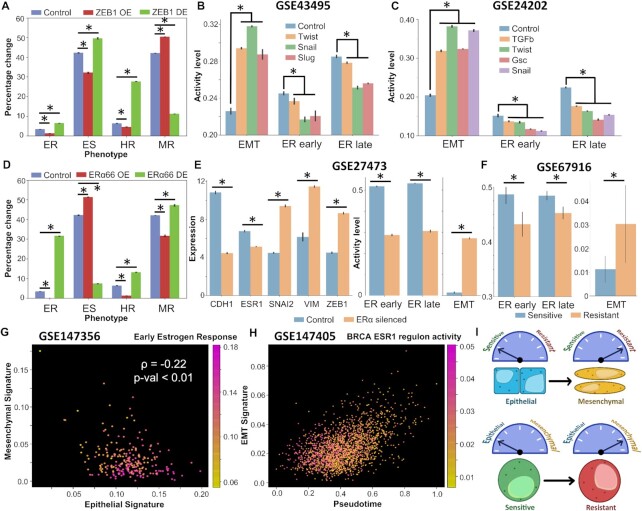
Figure 3.
Induction of EMT can drive suppression of estrogen signaling and vice versa. (A) Impact of over-expression/down-expression of ZEB1 levels in RACIPE simulations on frequencies of different biological phenotypes. Error bars denote standard deviation across n = 3 replicates. (B) Experimental data (GSE43495) for EMT induction via Twist, Snail or Slug in HMLE cells and the concurrent decrease in the magnitude of early and late estrogen response. (C) Experimental data showing EMT induction via TGFβ, Twist, Gsc and Snail in HMLE epithelial cells and the concurrent decrease in the magnitude of early and late estrogen response (GSE24202). (D) Same as (A) but for over-expression/down-expression of ERα66. (E) Experimental data showing differences in gene expression levels of Cdh1, Vim, Snai2 (Slug), Vim and Zeb1 and change in magnitude of early and late estrogen response and the EMT program (ssGSEA on MSigDB hallmark EMT signature) in control and ERα silenced MCF7 cells (GSE27473). (F) Experimental data showing differences in activity levels of early ER response, late ER response and EMT program in sensitive and resistant MCF7 cell lines (GSE67916). For A–F, * denotes a statistically significant difference between the control and perturbed/induced case assessed by a two-tailed Student’s t-test assuming unequal variances. (G) Scatter plot showing association between activity of early estrogen response and cells with varying positions on a 2D epithelial–mesenchymal plane (GSE147356). Spearman’s correlation coefficient between epithelial and mesenchymal scores, and corresponding P-value are reported. Color bar represents the activity of early estrogen response. (H) Scatter plot showing activity of EMT signature in TGFβ treated MCF7 individual cells in pseudo time and the concurrent decrease in BRCA ESR1 regulon activity. Color bar represents the range of activity level of the ESR1 regulon (GSE147405). (I) Schematic showing bidirectional associations between the EMP and the drug resistance program, i.e. induction of EMT drives a switch to a therapy-resistant state, and acquisition of therapy resistance often drives EMT.