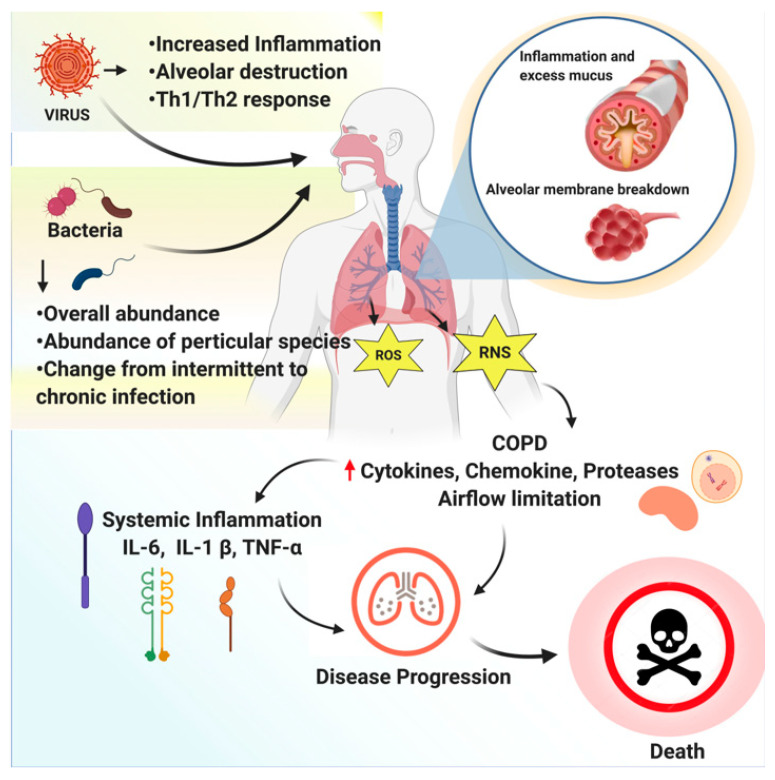
Figure 1.
An overview of respiratory tract infections caused by bacteria and viruses. Respiratory pathogens increase the chance of intermittent to chronic lung infection by increasing inflammation and alveolar destruction. Generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) leads to increase cytokines, chemokines, protease, and limitation of airflow that induce the severity and progression of COPD, systemic inflammation, and lung disease progression and decrease patient survival.