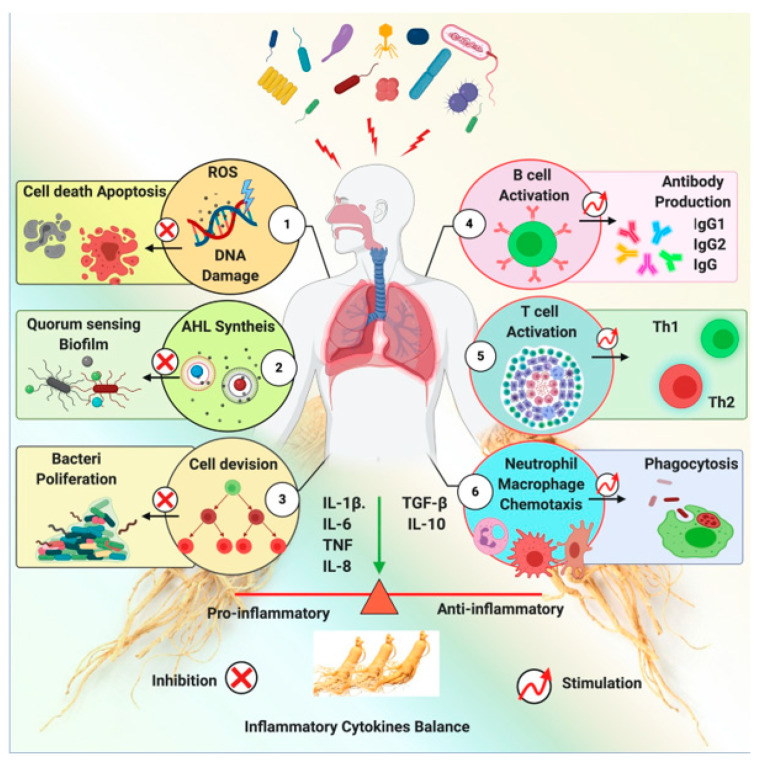
Figure 6.
Ginseng and its derived components’ anti-bacterial effects via multiple mechanisms. (1) Ginseng inhibits the DNA damage and apoptosis by inhibition of ROS, (2) suppresses AHL-(acyl homoserine lactones) leading to the inhibition of quorum sensing biofilm formation of bacteria, (3) inhibits cell division and bacterial proliferation, (4) stimulates B cell activation and antibody production, (5) activates Th1 and Th2 response, (6) ginseng enhances phagocytosis of Neutrophil and macrophage [37].