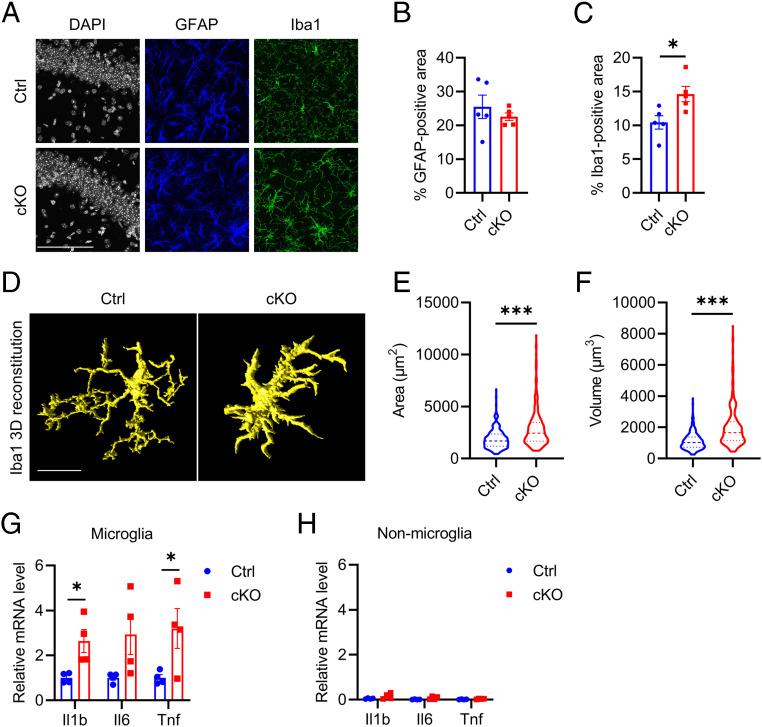
Fig. 1.
Atg7 loss of function induces microgliosis and increases proinflammatory cytokines level in vivo. (A) Representative immunofluorescence images of astroglial marker (GFAP), microglial marker (Iba1) in brains of littermate control, and Atg7 cKO mice 3 mo after tamoxifen injection (5 mo of age). (Scale bar, 100 μm.) (B and C) Quantification of GFAP (B)- and Iba1 (C)-positive area in A. Two-tailed Student’s t test. (n = 4/group). (D) Representative three-dimensional rendering of Iba1 immunostaining in the brains of control and Atg7 cKO mice. (Scale bar, 10 μm.) (E and F) Quantification of microglial cell surface area (E) and cell volume (F). Two-tailed Student’s t test (>200 cells from n = 4/group). (G and H) qPCR measurement of mRNA levels of proinflammatory cytokines (Il1b, Il6, and Tnf) in sorted microglial (G) and nonmicroglial (H) cell population from the brains of control and Atg7 cKO mice 3 wk after tamoxifen injection (10 wk of age). Two-tailed Student’s t test. (n = 4/group). Data are presented as mean ± SEM. *P ≤ 0.05; ***P ≤ 0.001.