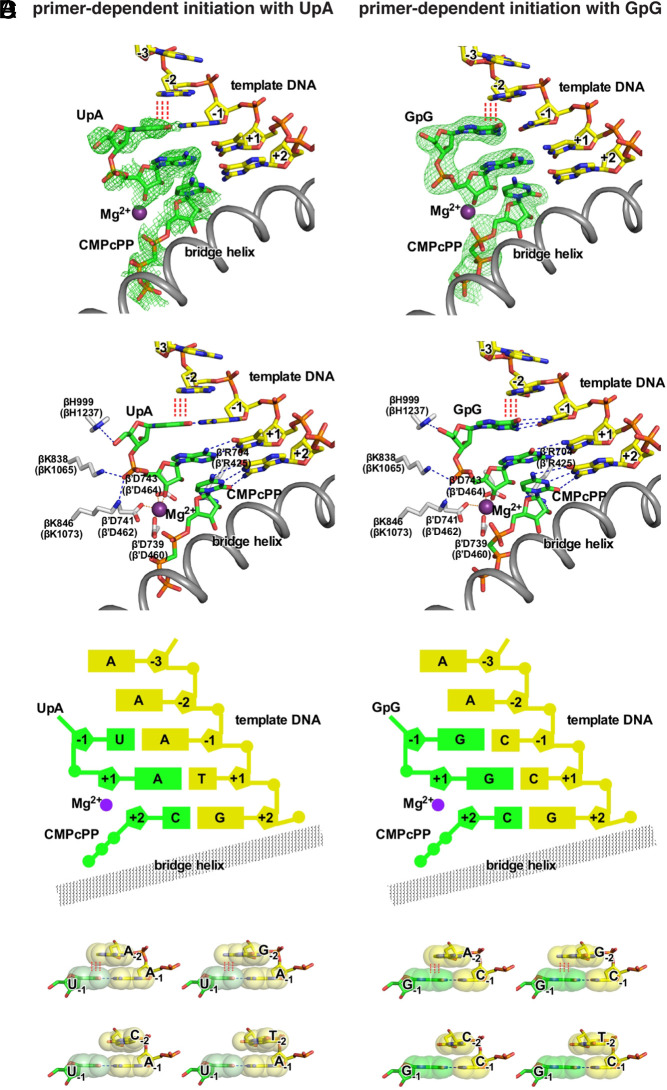
Fig. 7.
Structural basis of promoter-sequence dependence of primer-dependent initiation at position TSS−2. Crystal structures of T. thermophilus RPo[ATSS−2ATSS−1TTSS]-UpA-CMPcPP (Left) and T. thermophilus RPo[ATSS−2CTSS−1CTSS]-GpG-CMPcPP (Right). (A) Experimental electron density (contoured at 2.5 σ; green mesh) and atomic model for the DNA template strand (yellow, red, blue, and orange for C, O, N, and P atoms), dinucleotide primer and CMPcPP (green, red, blue, and orange for C, O, N, and P atoms), RNAP active-center catalytic Mg2+(I) (violet sphere), and RNAP bridge helix (gray ribbon). (B) Contacts of RNAP residues (gray, red, and blue for C, O, and N atoms) with primer and RNAP active-center catalytic Mg2+(I). RNAP residues are numbered both as in T. thermophilus RNAP and as in E. coli RNAP (in parentheses). (C) Schematic summary of structures. Template-strand DNA (yellow); primer and CMPcPP (green); RNAP bridge helix (gray); RNAP active-center catalytic Mg2+(I) (violet). (D) Structural basis of promoter-sequence dependence at position TSS−2. Extensive interchain base stacking of template-strand purine, A or G, with the 5′ nucleotide of primer (upper row; red vertical dashed lines) and limited interchain base stacking of template-strand pyrimidine, C or T, and the 5′ nucleotide of primer (lower row). The interchain base-stacking patterns of template-strand A with primers UpA and GpG are as observed in structures of RPo[ATSS−2ATSS−1TTSS]-UpA-CMPcPP and RPo[ATSS−2CTSS−1CTSS]-GpG-CMPcPP (A–C); the interchain base-stacking pattern of template-strand T with primer GpG is as observed in structure of RPo[TTSS−2CTSS−1CTSS]-GpG-CMPcPP (SI Appendix, Fig. S7); the other interchain base-stacking patterns are modeled by analogy. Base atoms are shown as van der Waals surfaces. Colors are as in A.