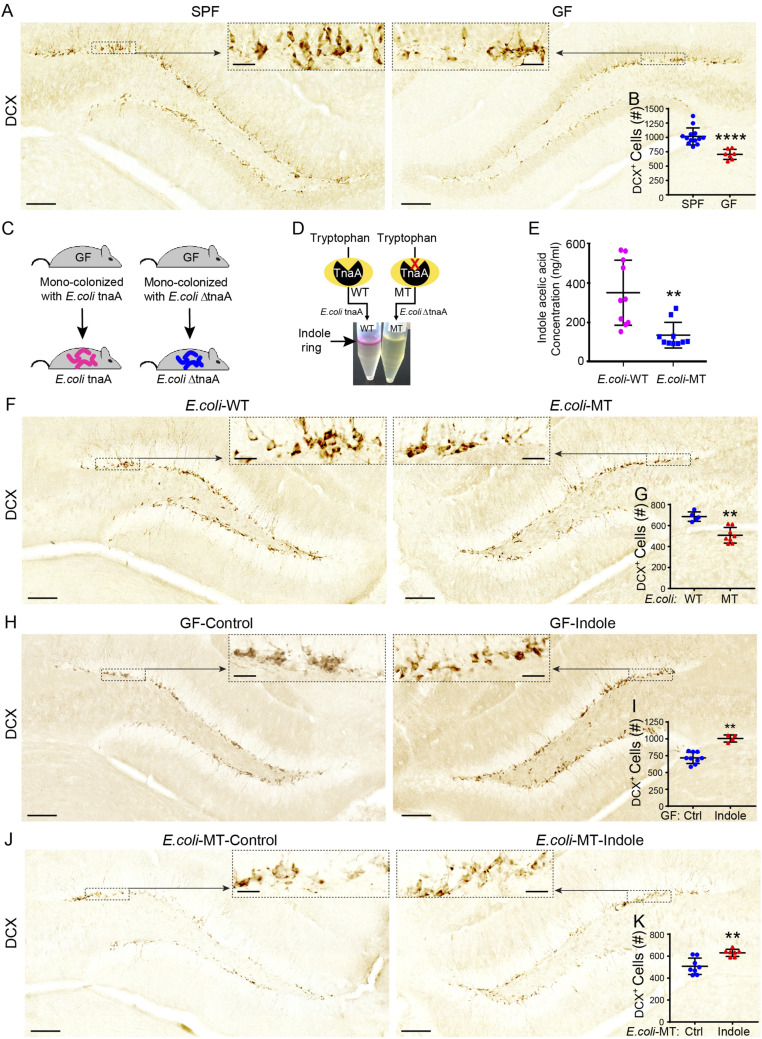
Fig. 1.
Exposure to indole rescues neurogenesis deficits in “indole-deficient” GF and mutant E. coli monocolonized mice. (A) Representative images of DCX-DAB–stained immature neurons in the DGs of SPF and GF male mice. The black dashed boxes indicate the comparative areas that are magnified to show the notable increase in DCX+ neurons. (B) DCX+ immature neuron populations are significantly reduced in the DGs of GF (n = 7) compared with SPF (n = 13) male mice. (C) Male and female GF mice were inoculated with WT E. coli tnaA or mutated E. coli ΔtnaA and their progeny maintained in a controlled environment until experimental testing. (D) WT and MT E. coli indole production was qualitatively assessed by Kovac’s assay, whereby the presence of indole is indicated by the presence of a pink color change in the alcohol layer of the reaction mixture. (E) Liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry analysis showing concentration of indole acetic acid is significantly reduced in serum of MT E. coli compared with WT E. coli male mice (n = 10/group). (F) Representative images of DCX-DAB–stained immature neurons in the DGs of WT E. coli and MT E. coli mice. The black dashed boxes indicate comparative areas that are magnified for clarity. (G) DCX+ immature neuron populations are significantly reduced in the DGs of MT E. coli mice (n = 8) compared with WT E. coli male mice (n = 5). (H) Representative images of DCX-DAB–stained immature neurons in the DGs of GF male mice treated with sham or indole-supplemented drinking water (200 μM) for 5 wk. The black dashed boxes indicate comparative areas that are magnified for clarity. (I) DCX+ immature neuron populations are significantly increased in the DGs of male GF mice supplemented with indole (n = 4) compared to vehicle drinking water (n = 9). (J) Representative images of DCX)-DAB–stained immature neurons in the DGs of MT E. coli male mice treated with sham or indole-supplemented drinking water (200 μM) for 5 wk. The black dashed boxes indicate comparative areas that are magnified for clarity. (K) DCX+ immature neuron populations are significantly increased in the DGs of MT E. coli male mice supplemented with indole (n = 7) compared with vehicle drinking water (n = 8). In all images, nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). (Scale bars: 100 μm.) All data are presented as mean ± SEM. Statistical differences were determined using Mann–Whitney U test (B, G, I, and K) and Student’s t test (E). Asterisks indicate a significant difference between groups (****P < 0.0001, **P < 0.01).