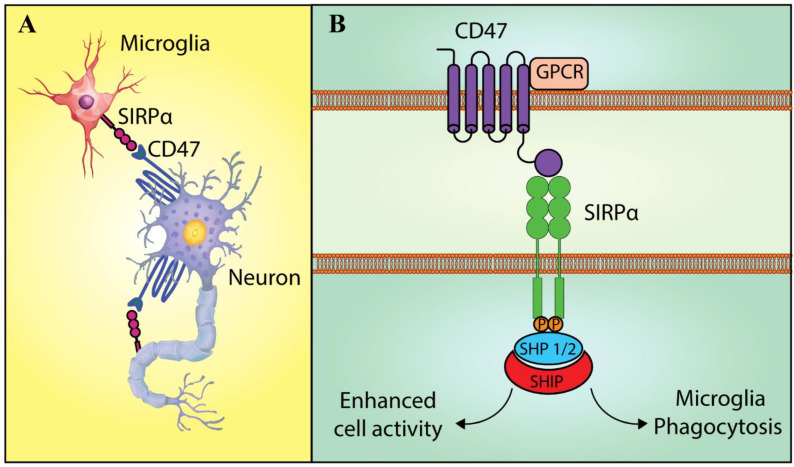
Figure 2.
The cell-to-cell cross-talk via the SIRPα-CD47 signaling. (A) Bi-directional signaling between CD47 and SIRPα. CD47 and SIRPα are possibly co-expressed on a similar cell and their ligation could mediate the inter-cellular signaling in a bi-directional manner. Even though SIRPα-CD47 signaling in the microglia is incompletely understood, the specific contribution of SIRPα and CD47 has been examined. Moreover, CD47 and SIRPα interactions could be observed in the phagocytic function of the microglia. (B) SIRP signaling in microglia. SIRPα phosphorylation enables the docking and the recruitment of SHP-1 and SHP-2. In this regard, various studies have shown that SHP-1 and SHP-2 perform opposite biological functions. Different signaling pathways have been negatively regulated by SHP-1 for the inhibition of numerous cell functions like phagocytosis. On the contrary, events affecting the cellular activity such as migration, as well as growth, have been shown to be positively regulated by SHP-2 [5]. Abbreviation: GPCR: G protein-coupled receptor, SIRPα: Signal regulatory protein α, SHP 1/2: SH2 domain-containing phosphatases 1 and 2, SHIP: SH2 domain-containing inositol phosphatase.