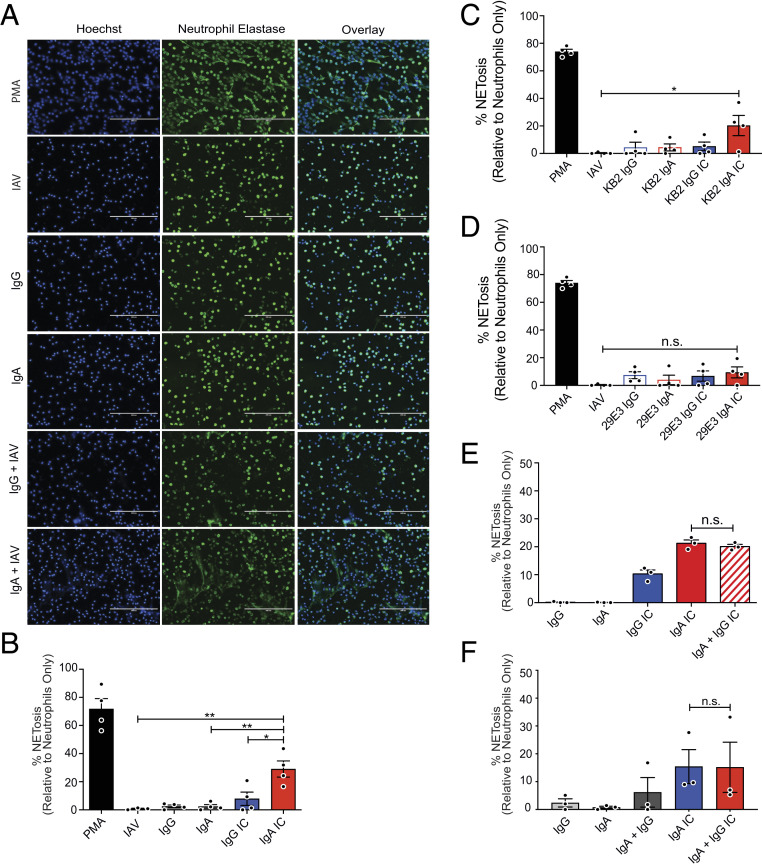
Fig. 1.
IgA–IAV ICs potentiate NETosis. (A–F) Primary human neutrophils were isolated from the peripheral blood of healthy donors (n = 3 or 4) and stimulated with PMA, monoclonal or polyclonal IgG or IgA antibodies, or ICs for 3 h as shown. NETosis was assessed by immunofluorescence microscopy after costaining for DNA (Hoechst) and neutrophil elastase. (A) Representative images are shown (20×). (Scale bars, 200 µm.) (B) The percentage of cells that had undergone NETosis (defined by typically NET morphology and costaining of DAPI + neutrophil elastase) was quantified in a blinded manner from five fields in four independent experiments. (C and D) The assay was repeated using monoclonal antibodies, (C) KB2 and (D) 29E3, which bind the HA stalk and head domain of Cal/09, respectively. (E and F) To determine the phenotype of mixed IgG/IgA ICs, polyclonal IgG and IgA were mixed with Cal/09 at (E) a 1:1 ratio or (F) at the ratio naturally found in serum. For all experiments, percent NETosis was normalized to unstimulated neutrophils. Three or four independent neutrophil donors were used for each experiment. Means and SE (SEM) of independent experiments are shown. Statistical significance was determined using one-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.