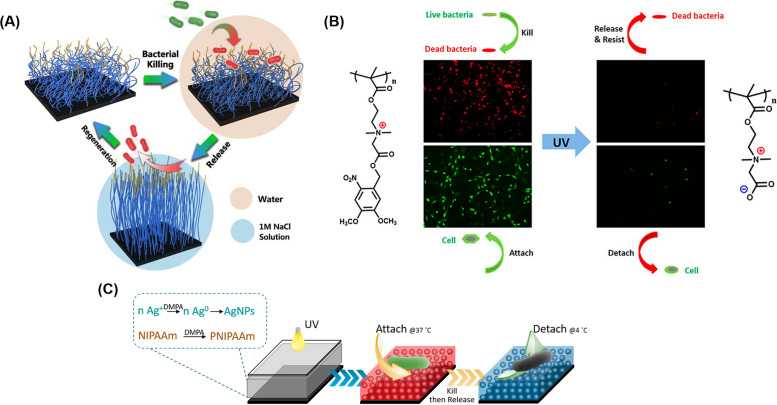
FIG. 5.
Smart hydrogels for antifouling: (a) using a salt-responsive surface based on a polyzwitterionic polymer, the contact angle decreased when the solution changed from water to 1 M NaCl solution; thus, bacteria were killed in water and released in salt water.119 Reprinted with permission from Huang et al., Chem. Eng. J. 333, 1–10 (2017). Copyright 2017Elsevier. (b) The surface of hydrogel based on photoresponsive polymer, poly[2-((4,5-dimethoxy-2-nitrobenzyl)oxy)-N-(2-(methacryloyloxy)ethyl)-N,N-dimethyl-2-oxoethan-1-aminium] (polyCBNA), was switched from cationic antibacterial to zwitterionic antifouling by UV treatment.58 Reproduced with permission from Liu et al., Langmuir 35(5), 1450–1457 (2019). Copyright 2018 American Chemical Society. (c) A thermosensitive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAAm) hydrogel encapsulating AgNPs was prepared via a photopolymerization method. As temperature changed from 37 °C to 4 °C, the surface switched from killing to repelling bacteria mode.117 Reproduced with permission from Yang et al., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8(41), 28047–28054 (2016). Copyright 2016 American Chemical Society.