Fig. 3.
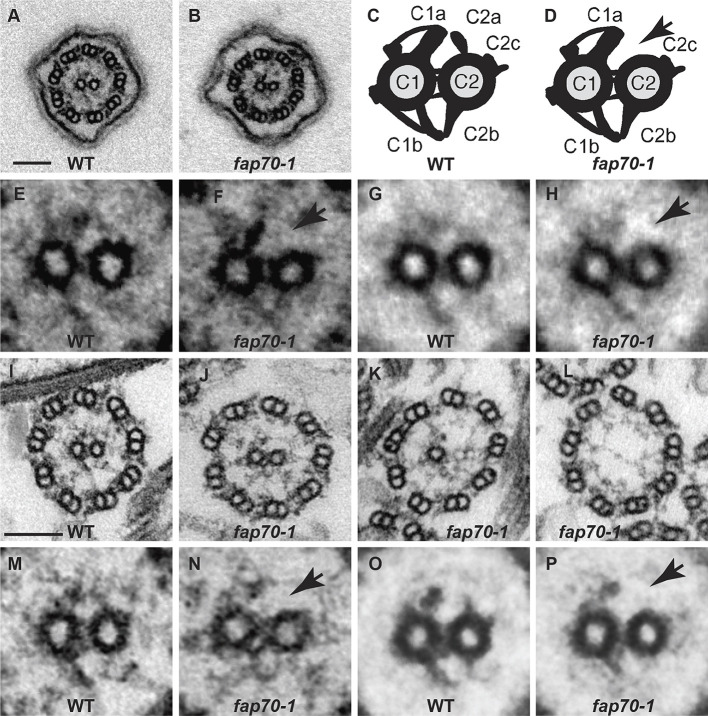
Loss of FAP70 causes ablation of the C2a projection. (A,B) Representative cross-sections of intact in situ flagella of wild-type (WT) and fap70-1 cells, respectively, as imaged by conventional TEM. All flagella of both strains had axonemes with nine DMTs and two central microtubules. (C,D) Diagrams of cross-sections of CAs of wild type and fap70-1, respectively, illustrating the C1 and C2 microtubules connected by bridge structures and with major projections (C1a, C1b, C2a, C2c and C2b) normally visible by conventional TEM labeled. The fap70-1 CA appears to lack the C2a projection (arrow in D). (E,F) Enlargement of CAs from panels A and B, respectively. The C2a projection appears to be absent from the fap70-1 CA (arrow in F). (G,H) Image averages based on six wild-type (G) and six fap70-1 (H) CAs of intact in situ flagella showing the apparent absence of the C2a projection in the fap70-1 flagellum (arrow in H). (I-L) Representative cross-sections of isolated axonemes from wild type (I) and fap70-1 (J-L). Some cross-sections of fap70-1 axonemes lacked one (K) or both (L) central microtubules. (M,N) Enlargement of CAs from panels I and J, respectively. The C2a projection appears to be absent from the fap70-1 CA (arrow in N). (O,P) Image averages based on six wild-type (O) and six fap70-1 (P) CAs of isolated axonemes showing the apparent absence of the C2a projection in the fap70-1 axoneme (arrow in P). Scale bars: 100 nm.