Fig. 6.
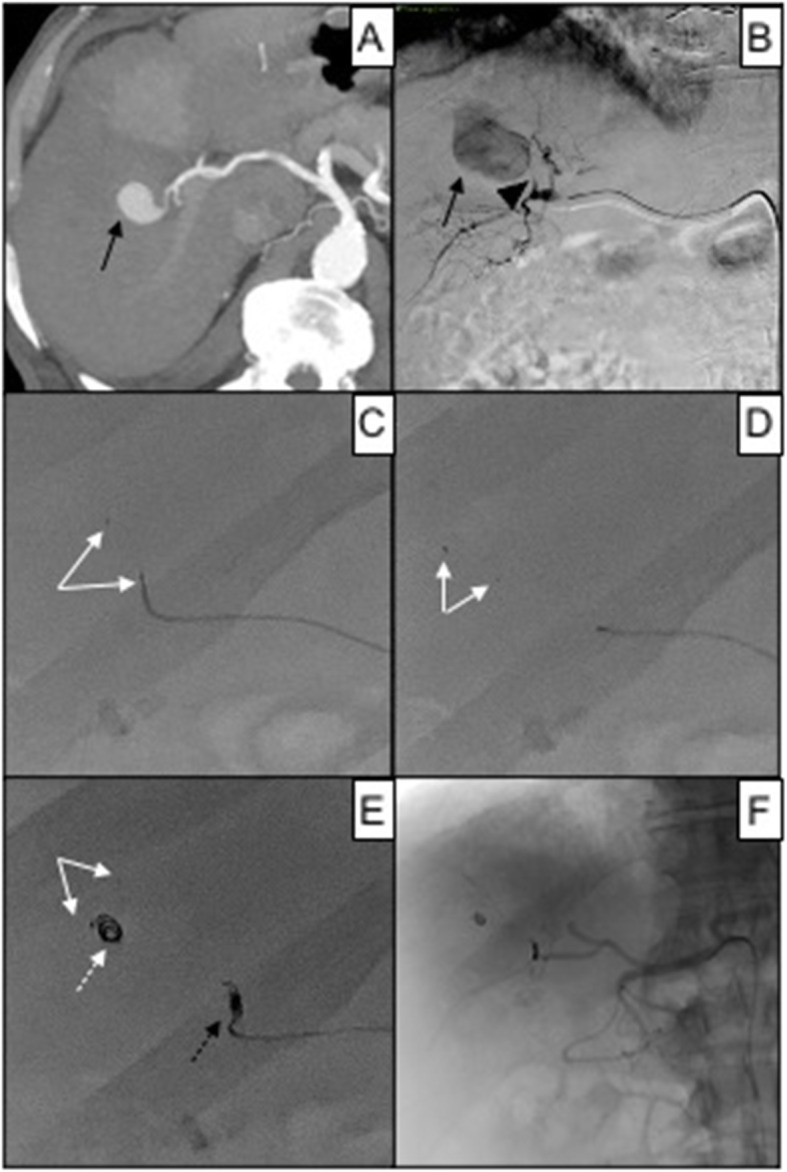
83 years old female affected by iatrogenic pseudoaneurysm of the right hepatic artery after RFA for HCC. In A, a contrast-enhanced CT scan in arterial phase shows the intraparenchymal vascular lesion (black arrow); in B, superselective DSA of the right hepatic artery confirms pseudoaneurysm (black arrow) refurnished by a short arterial feeder (black arrowhead); in C, attempt to perform MVP-3 (white arrows) embolization, target vessel caliper 1.1 mm; in D, due the shortness of the arterial feeder, MVP-3 (white arrows) migrated into the pseudoaneurysm sac; in E, proper embolization was obtained with a 2 mm Concerto® Medtronic controlled detachment coil (black dotted arrow), after that another pushable coils (white arrow) migrated into the pseudoaneurysm sac together with MVP (white arrow); in F, fluoroscopic control showing resolution of the pseudoaneurysm
