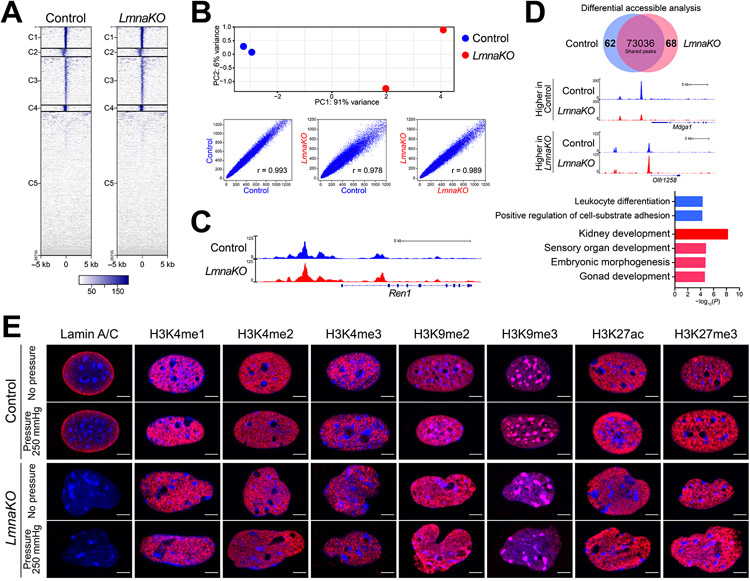
Figure 7. Lamin A/C regulates chromatin organization in renin cells.
A, Heatmaps showing normalized ATAC-seq signal intensity around the transcription start site (TSS) in control cells and cells with deletion of the Lmna gene (LmnaKO). B, LmnaKO cells showed a difference in accessible chromatin compared to controls. Principal component analysis (PCA) with identified ATAC-seq peaks in 2 replicates of each group and the Pearson correlation coefficient clearly separated samples of each group. C, Images of peaks of the accessible chromatin at the Ren1 regulatory locus. D, The differential accessible analysis identified 62 and 68 peaks in the control and LmnaKO cells, respectively. The images show representative loci of the differential accessible regions. Gene Ontology (GO) analysis identified enriched categories on genes associated with peaks significantly higher in control (blue) and higher in LmnaKO (red). E, Immunocytochemistry for lamin A/C, H3K4me1, H3K4me2, H3K4me3, H3K9me2, H3K9me3, H3K27ac, and H3K27me3 shown in red and nuclear staining with Hoechst in blue in renin cells with or without LmnaKO subjected to pneumatic pressure. Scale bar, 5 μm.