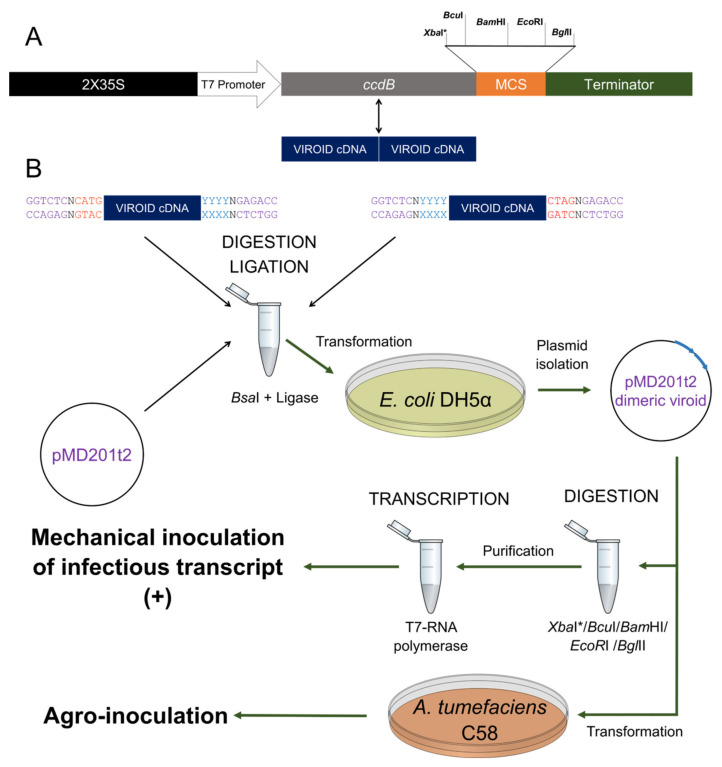
Figure 1.
Generation of head-to-tail dimeric viroid cDNAs into pMD201t2. (A) Scheme of the transcriptional unit (TU) designed for generating dimeric viroid RNAs in vitro or in vivo by agro-inoculation. This TU which consists of a duplicated 35S followed by a T7 promoter, the lethal gene ccdB and the PoPit terminator preceded by a multiple cloning site (MCS). In the cloning process, the dimeric viroid cDNA sequence replaces the lethal gene, therefore being a highly efficient reaction. (B) Viroid sequences are amplified with two pairs of primers containing the BsaI recognition site (purple) designed to generate compatible ends between the viroid cDNA (blue) and to the plasmid (red). The dimeric viroidal cDNA cloned into pMD201t2 can be used to generate the infectious RNA transcript in vitro, using T7 RNA polymerase onto a linearized plasmid (digested with BcuI, BamHI, EcoRI BglII, and XbaI*). Additionally, the pMD201t2-viroid can be transformed into Agrobacterium tumefaciens for transient plant transformation and subsequent production of infective viroid RNAs in vivo. * If the viroid cDNA sequence ends in T.