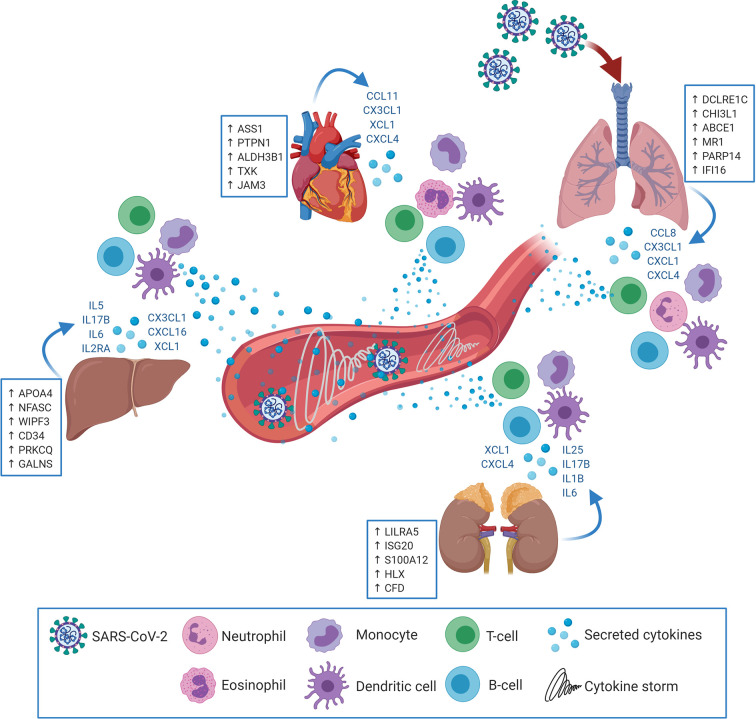
Figure 7.
SARS-CoV-2 may target extrapulmonary tissues along pulmonary tissues thereby inducing transcriptional shifts in the expression of central immune regulators (examples in the blue boxes; putative biomarkers unique for each tissue). Consequently, pulmonary as well as extrapulmonary tissues may secrete cytokines and immune mediators (in blue font) resulting in the chemoattraction and activation of innate and adaptive immune cells (e.g. Neutrophils, eosinophils, monocytes, dendritic cells, T-cells and B-cells). Upon activation, the infiltrating immune cells begin to uncontrollably secrete additional cytokines and immune mediators which elicits the cytokine storm and system inflammation phenomena.