Fig 1.
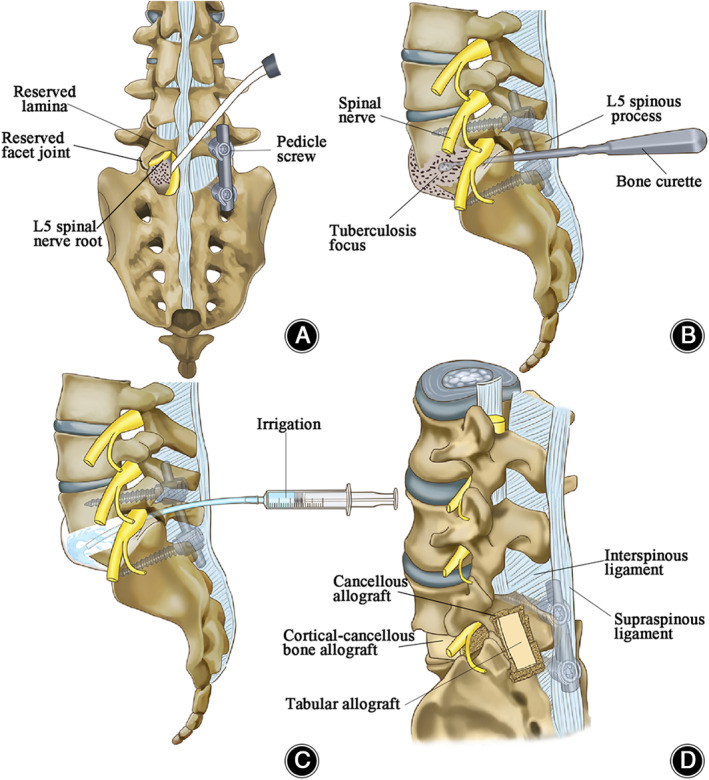
Schematic diagram indicating the dominating surgical process. (A) The access to the tuberculosis focus. After pedicle screws and titanium rod were inserted, limited unilateral vertebral plate was removed to establish an operational pathway that facilitated the access to spinal tuberculosis lesion and under direct vision protected the dura and nerve roots from injury. The zygapophyseal joint and part of the lamina were reserved. (B) The elimination of tuberculosis focus. Once the approach to the tuberculosis focus was established via the intervertebral space, the abnormal intervertebral disc and sclerosed dead bone, as well as necrotic tissue and inflammatory granuloma, were removed by bone curette during procedure of debridement, reaching healthy bone interface with blood oozing out. (C) Lesion irrigation. After examination of the dural sac, we confirmed there was no damage. The tubercular cavity is irrigated in sequence of physiological, saline‐hydrogen peroxide and reduplicative physiological saline for intensive clearance of the wound. (D) Posterolateral view of allogenic bone transplantation. Before bone transplantation, the reserved lamina is decorticated, trimmed bulk cortical–cancellous bone allograft was filled into the cavity and support the space between the L5‐S1 vertebral bodies. Also, the deficient laminectomy was coated by the tabular allograft coverage. After the procedure, the spinous process, the interspinous ligament, and the supraspinous ligament are preserved.
