FIGURE 1.
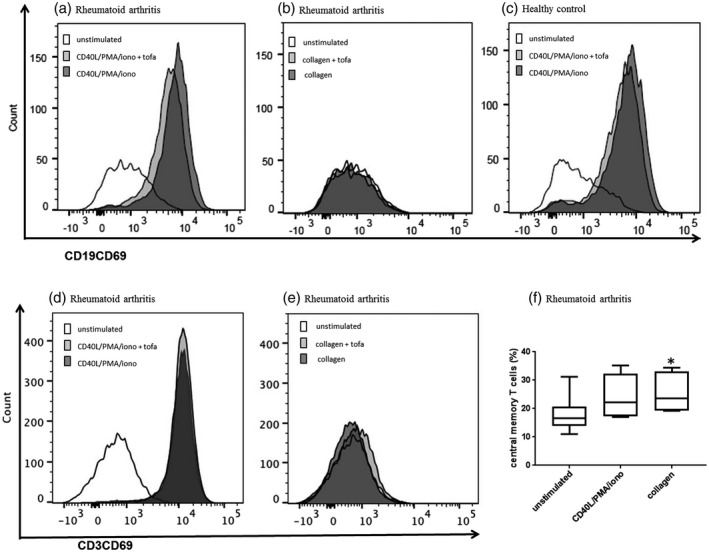
Activation of B and T cells. The percentages of B cells expressing CD69 activation marker significantly increased after CD40L/phorbol myristate acetate (PMA)/ionomycin stimulation in both rheumatoid arthritis (a, P < 0.0001 versus unstimulated) and in healthy subjects (c, P = 0.004 versus unstimulated) but not after collagen epitope stimulation (b). Tofacitinib treatment weakly reduced CD69+ B cells. CD69 significantly increased in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) T cells after non‐specific lymphocyte stimulation (d, P = 0.006) but not after collagen epitope stimulation (e). Tofacitinib treatment did not significantly decrease T cell activation mirrored by CD69 surface expression. Collagen epitope stimulation increased significantly the proportion of RA central memory T cells (f, P = 0.049)
