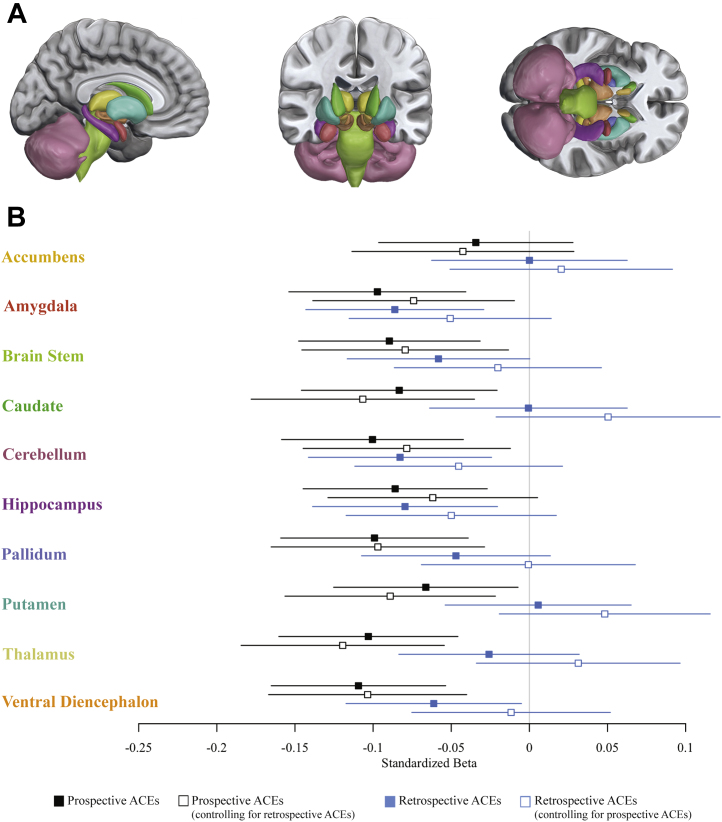
Figure 3.
Associations between childhood adversity and subcortical gray matter volume. (A) The 10 subcortical structures for which gray matter volume was estimated. (B) Standardized effect sizes (β and 95% confidence intervals) for associations between prospectively ascertained adverse childhood experiences (ACEs) and retrospectively reported ACEs with average gray matter volume of 10 subcortical structures. Solid squares mark standardized effect sizes for the independent associations between prospectively ascertained and retrospectively reported ACEs and age-45 brain structure, whereas open squares mark standardized effect sizes for the associations between prospectively ascertained and retrospectively reported ACEs and age-45 brain structure when controlling for the other ACEs measure.