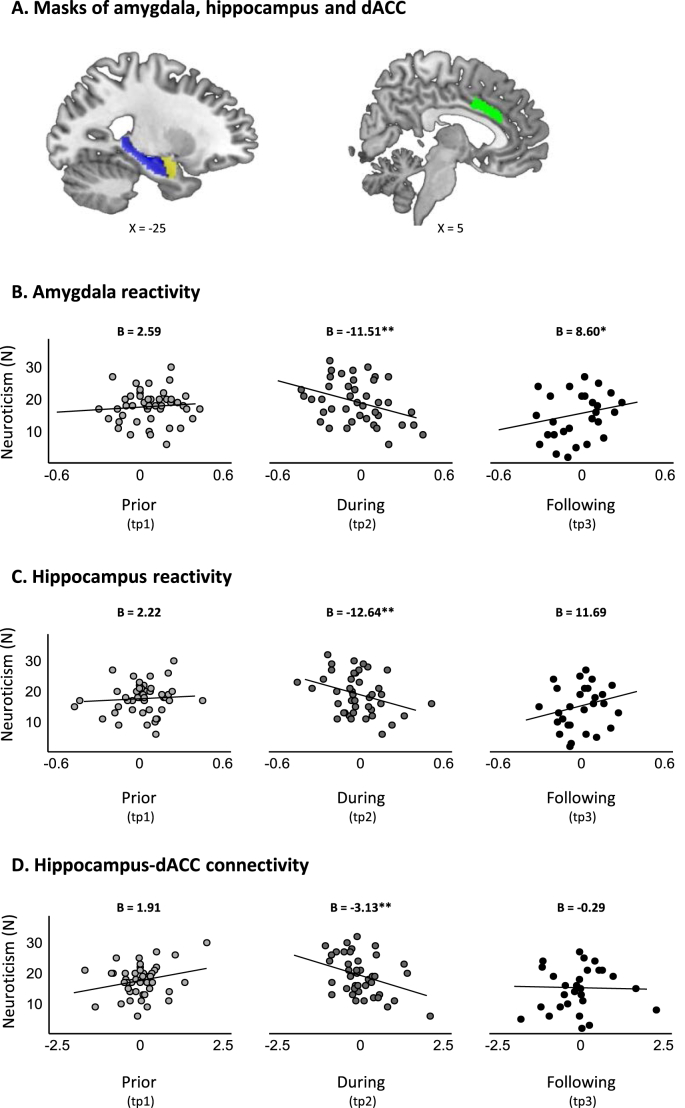
Fig. 3.
Dynamics in neuroticism and limbic reactivity. A) Masks of three anatomically defined ROIs. Anatomical masks of the amygdala (yellow) and hippocampus (blue) were defined using the Automated Anatomical Labeling atlas (AAL) (Tzourio-Mazoyer et al., 2002), and the mask of the dACC (green) was defined using the Destrieux Atlas (2009) as implemented in neurovault (https://identifiers.org/neurovault.image:23264). (B–D) Scatter plots of the association between neuroticism scores and limbic reactivity in response to the Medical83 condition over the three time points of assessment. B) Linear mixed effects (LME) model for amygdala reactivity revealed a significant time by amygdala activation interaction (F(2, 99.84) = 6.21, p = .002), driven by time-dependent relationship between neuroticism and amygdala activation such that elevated neuroticism during military service was associated with reduced amygdala activation at that time (B(tp2) = −11.51, p = .002), while elevated neuroticism following discharge was associated with increased amygdala activation (B(tp3) = 8.60, p = .046). C) LME model for hippocampus reactivity revealed a significant time by hippocampus activation interaction (F(2, 101.12) = 4.81, p = .010), driven by time-dependent relationship between neuroticism and hippocampus activation such that elevated neuroticism during military service was associated with reduced hippocampus activation at that time (B(tp2) = −12.64, p = .005), while the association between elevated neuroticism following discharge and increased hippocampal activation was trending towards significance (B(tp3) = 11.69, p = .061). D) LME model for hippocampus-dACC connectivity revealed a significant time by hippocampus-dACC connectivity interaction (F(2, 103) = 4.14, p = . 018), driven by time-dependent relationship between neuroticism and hippocampus-dACC connectivity such that elevated neuroticism during military service was associated with reduced hippocampus-dACC functional connectivity (B(tp2) = −3.13, p = .008). In all panels, reactivity values were person-mean centered, representing intra-individual change. *indicates p < .05, **indicates p < .01. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)