Figure 4.
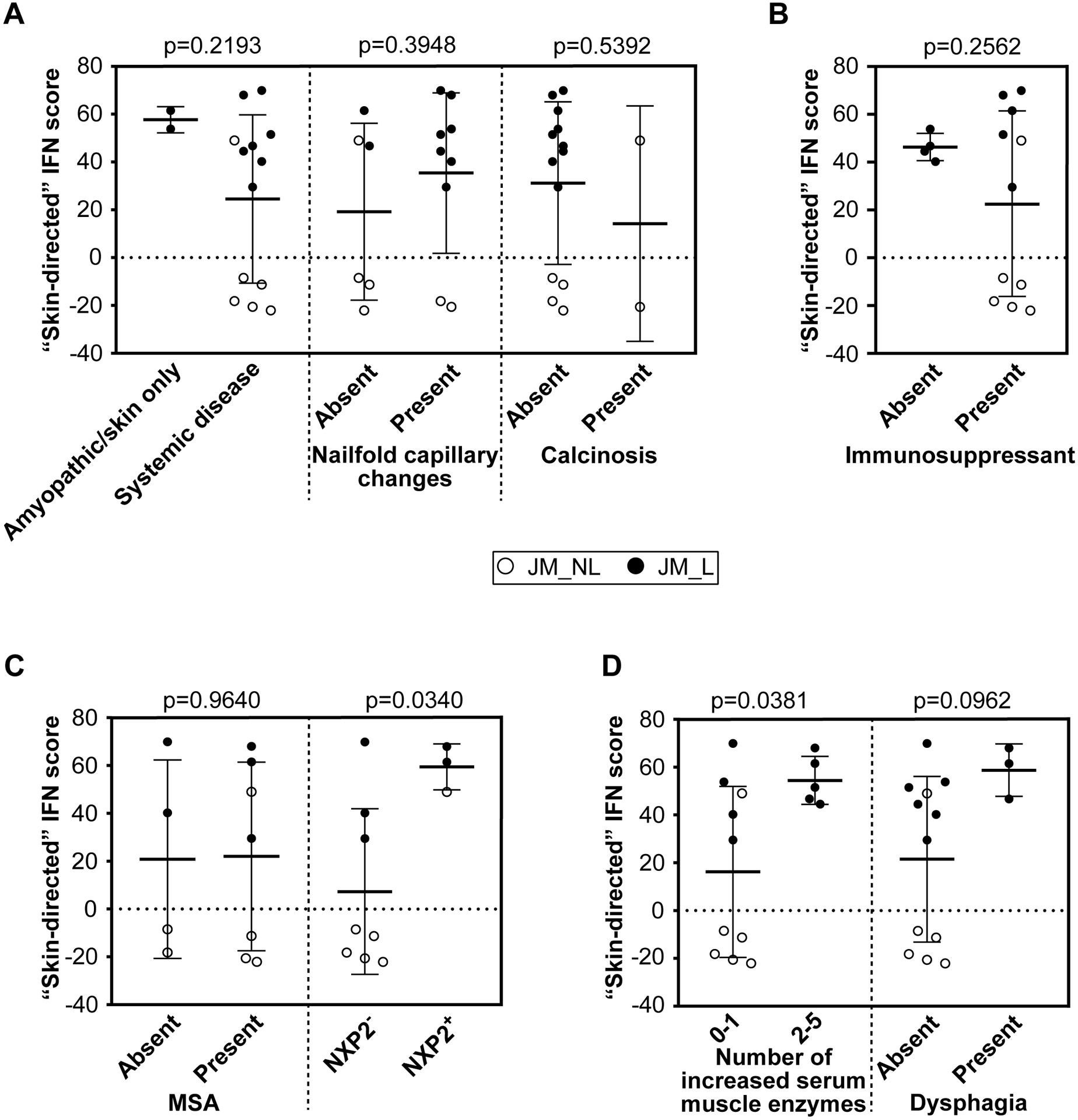
JM skin-directed IFN score with clinical variables. A. The skin-directed IFN score is not significantly modified by the presence of systemic disease, nailfold capillary changes or calcinosis. B. The skin-directed IFN score is not significantly changed by treatment status. C. The presence alone of any myositis-specific autoantibody (MSA) does not significantly alter the skin-directed IFN score; however, NXP2+ JM patients have a significantly higher skin-directed IFN score when lesional and non-lesional skin are analyzed together. D. An increased overall number of serum muscle enzymes was associated with a higher skin-directed IFN score (p-value=0.0381) when lesional and non-lesional skin are analyzed together. A higher skin-directed IFN score demonstrated a trend toward presence of dysphagia.
