Figure 1.
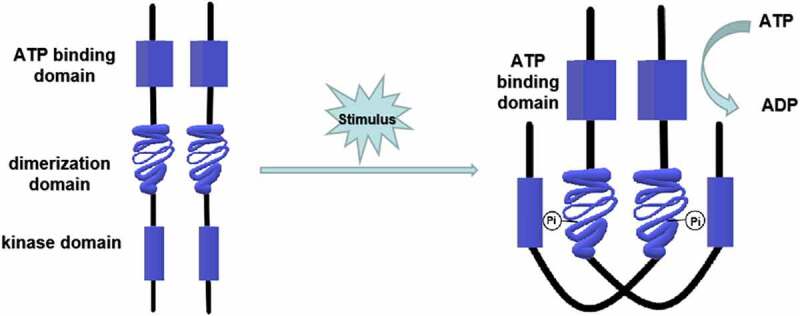
Structure and phosphorylation of HPK. The HPK is a dimer composed of two subunits. Each subunit contains an ATP binding domain, a dimerization domain, and a kinase domain (phosphorylation site). When the input domain of HPK is appropriately stimulated, the dimerization domain of one subunit will approach to the kinase domain of the other subunit to promote the phosphorylation
