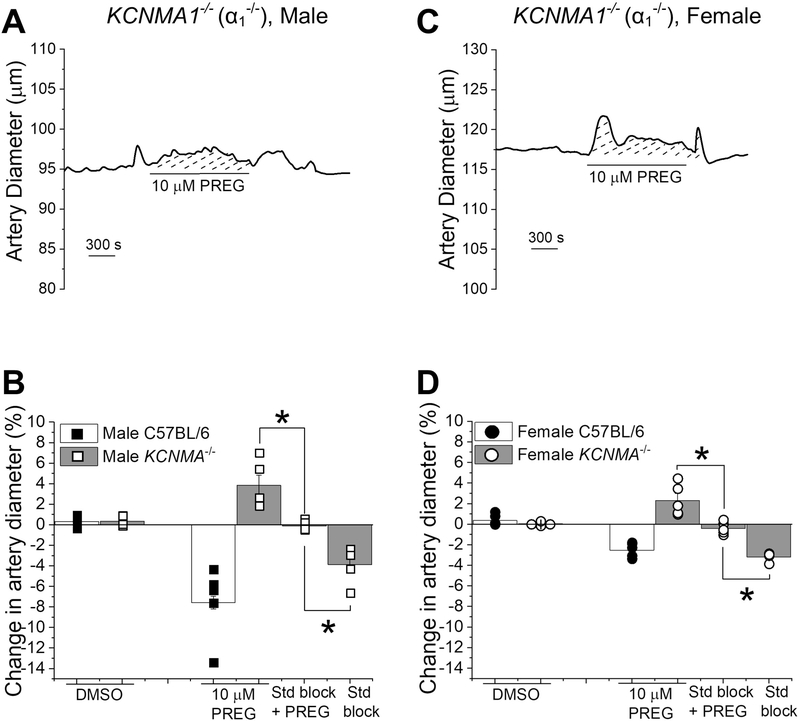
Figure 8. The absence of BK α subunits (slo1 proteins) prevents pregnenolone from constricting middle cerebral arteries.
A. Diameter trace showing the response of pressurized, de-endothelialized MCA segment from KCNMA1−/− male mouse to 10 μM PREG.
B. Comparison of arterial responses to 10 μM PREG in absence and presence of the steroid block, and DMSO in wt C57BL/6J and KCNMA1−/− male mice. Black squares indicate individual responses from male wt C57BL/6J; hollow squares indicate individual responses from male KCNMA1−/− mice. *Statistically significant difference from 10 μM PREG in presence of steroid receptor blockers (P= 0.00439, P= 0.00169 from left to right, Kruskal–Wallis test). C. Diameter trace showing the response of in pressurized, de-endothelialized MCA segment from KCNMA1−/− female mouse to 10 μM PREG. D. Comparison of the arterial response to 10 μM PREG in absence and presence of the steroid block, steroid receptor blockers, and DMSO in wt C57BL/6J versus KCNMA1−/− female mice. Black circles indicate individual responses from female wt C57BL/6J; hollow circles indicate individual responses from female KCNMA1−/− mice. *Statistically significant difference from 10 μM PREG in presence of the steroid block (P= 0.00607, P= 0.00002 from left to right, Kruskal–Wallis test); n=5 for each group. Each data point was obtained from a different MCA segment; all data-points within each group were obtained from separate mouse donors.