Extended Data Fig. 8 |. Effects of in vivo EP2 inhibition on macrophage metabolism, synaptic mitochondria and mitochondrial morphology in young and aged mice.
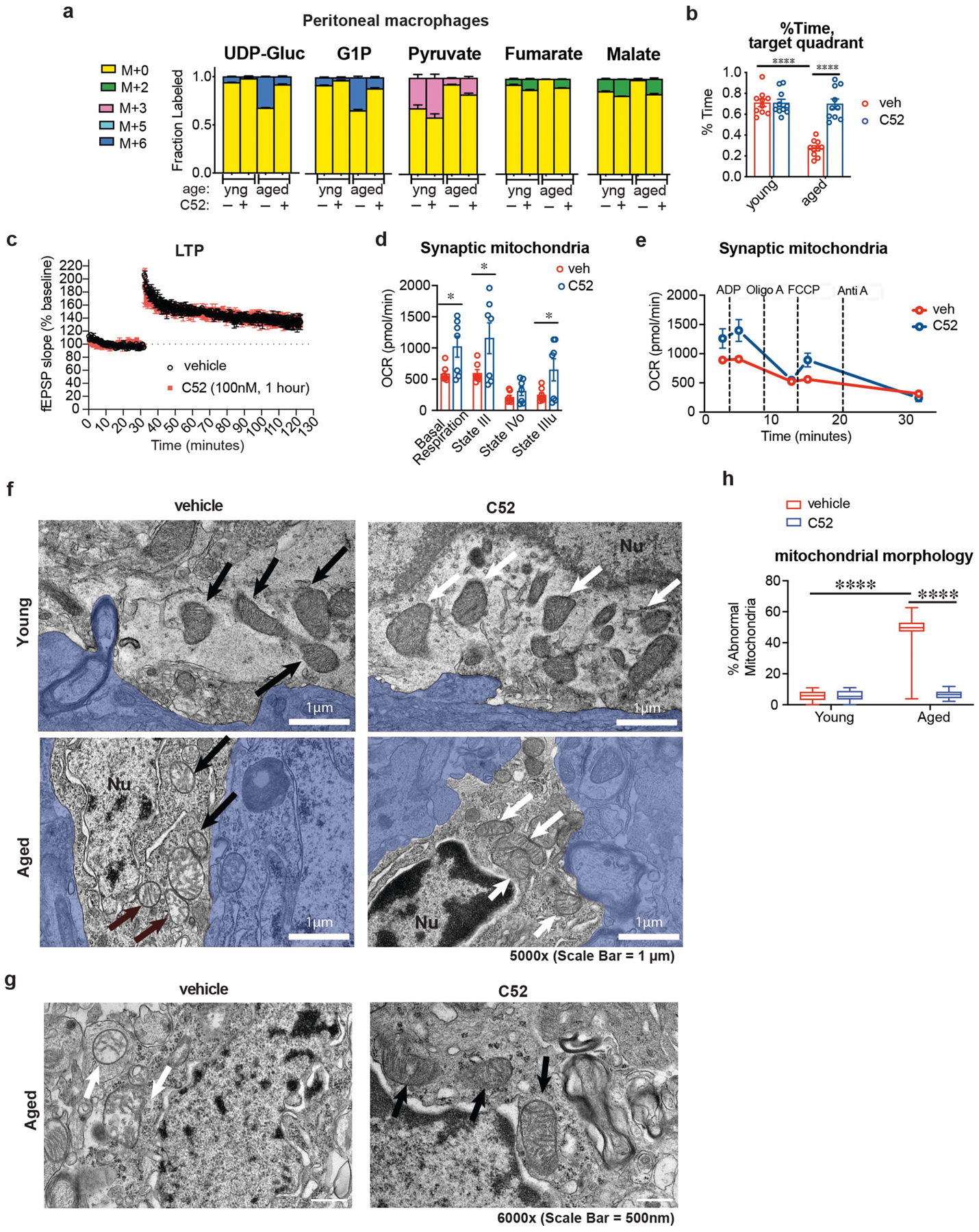
Data are mean ± s.e.m. unless otherwise specified. a, Peritoneal macrophage metabolite labelling following in vivo U-13C-Glucose isotope tracing (n = 6 mice per group). b, Quantification of per cent time in the target quadrant of the Barnes maze. Two-way ANOVA, effect of age or treatment ****P < 0.0001, Tukey’s post hoc test ****P < 0.0001 (n = 10 mice per group). c, Long-term potentiation (LTP) in the CA1 hippocampal region over a 120-min recording interval. Acute administration of C52 (100 nM, 1 h) before TBS does not alter LTP in aged mice (20–22 mo mice, n = 3 mice per group). d, Synaptic mitochondria were isolated from synaptosome fractions prepared from 16–month-old mice treated with or without C52 (10 mg/kg/d, 10 days). Coupling between the mitochondrial electron transport chain and oxidative phosphorylation (using succinate as the substrate) was determined using the Seahorse XFe24 analyser. Basal respiration (state II) and ADP-supplemented respiration (state III) reflect both electron transport and ATP generation and increased by twofold with EP2 blockade. Maximal respiration (state IIIu) after application of the H+ gradient uncoupler FCCP was also higher with EP2 inhibition, and state IVo, reflecting blockade of ATP synthase with oligomycin, was unchanged. *P < 0.05, two-tailed Student’s t-test (n = 7 mice per group). e, Coupling assay trace of synaptic mitochondria from aged mice treated with or without C52 for 10 days. Rates of basal complex II respiration as well as states III (ADP stimulated respiration), IV (oligomycin) and IIIu (FCCP) were consecutively measured (n = 7 mice per treatment group). f, TEM images at 5,000× magnification of microglia in the CA3 region of the hippocampus from young (3–4 months) and aged (22–24 months) mice treated with or without C52 (10 mg/kg/d, 1 month). Aged mice exhibit abnormal, non-electron-dense mitochondria; these features are rescued with C52 treatment. Arrows (black for vehicle, white for C52) point to mitochondria within microglia; blue shaded areas are non-microglial cells. Nu, nuclei; white scale bars, 1 μm. g, Higher-power representative TEM images of aged (22–24 months) mice treated with or without C52 (10 mg/kg/d, 1 month) showing differences in cristae and electron density. White scale bars, 500 nm. h, Quantification of per cent abnormal mitochondria in microglia of young (3–4 months) and aged (22–24 months) mice treated with or without C52 (10 mg/kg/d, 1 month); n = 66 mitochondria per group, 2-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test, ****P < 0.001.
