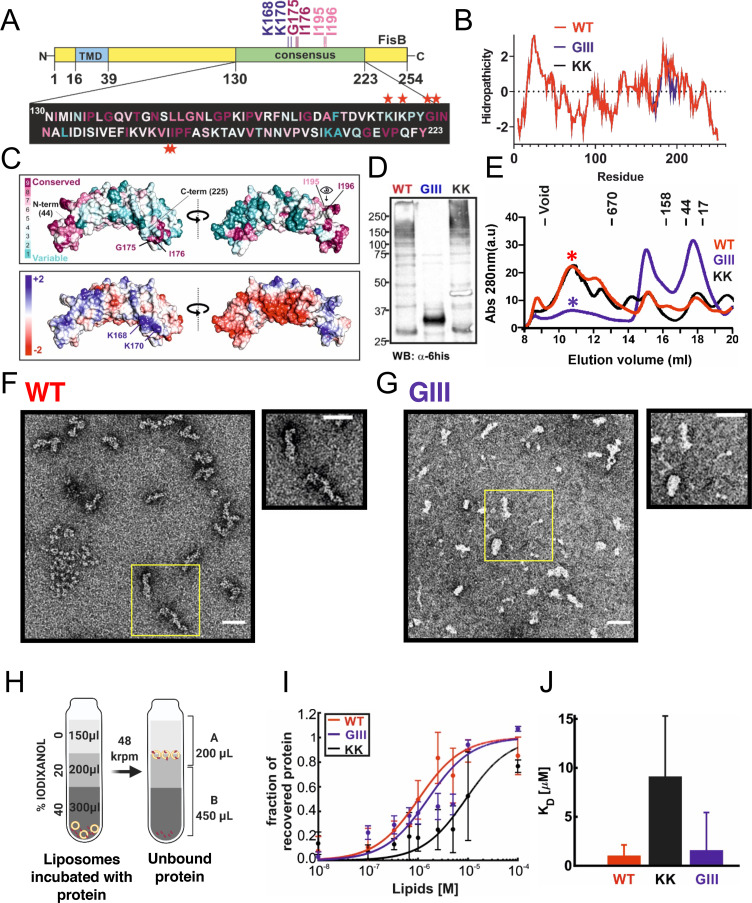
Fig 5. FisB mutants selectively impaired in oligomerization and membrane binding.
(A) Mutated residues shown on the FisB domain structure. (B) Kyle-Doolittle hydrophobicity profile of the FisB sequence for WT, FisB K168D, K170E (FisBKK), and FisB G175A,I176S, I195T, I196S (FisBGIII) mutants. (C) Mutations shown on the predicted model [49] of FisB44-225. Residue conservation (top) and electrostatic potential (bottom) are mapped onto the structure. (D) Western blot of cell lysates from E. coli cells expressing FisB-ECDWT, FisB-ECDGIII, or FisB-ECDKK, probed with an anti-histidine antibody. High molecular weight bands in the WT and KK lanes are largely absent in the GIII lane, indicating that FisBGIII is less prone to forming oligomers. (E) SEC of FisB WT and the GIII and KK mutants. Intensities of high and low molecular weight peaks are reversed for FisB WT and the GIII mutant, whereas the KK mutant has a profile similar to WT. (F) A fraction corresponding to the high-molecular peak in E (indicated by *) for FisB WT was collected and imaged using negative-stain EM, which revealed flexible, elongated structures approximately 50 nm × 10 nm. (G) A similar analysis for FisBGIII revealed more heterogeneous and less stable structures. Scale bars in F and G are 50 nm. (H) Schematic of the floatation experiments to determine the apparent affinity of FisB mutants for liposomes containing acidic lipids. Experiments and analyses were carried out as in Fig 4, except only 2 fractions were collected. iFluor555-FisB ECD (100 nM) was incubated with10−8 to 10−4 M lipids for 1 hour at room temperature before floatation. Liposomes contained 45 mole % of CL and 55% PC. (I) Fraction of protein bound to liposomes as a function of total lipid concentration. Data were fitted to a model as in Fig 4F. The data and fit for FisB WT are copied from Fig 4F for comparison. (J) Best fit values for Kd were 1.0 μM for WT (95% confidence interval, CI = 0.7–2.1 μM), 9.1 μM for KK (CI = 6.5–15.3 μM), and 1.6 for GIII (CI = 0.9–5.1 μM), respectively. EM, electron microscopy; FisB, fission protein B; PC, phosphatidylcholine; SEC, size exclusion chromatography; WT, wild-type.