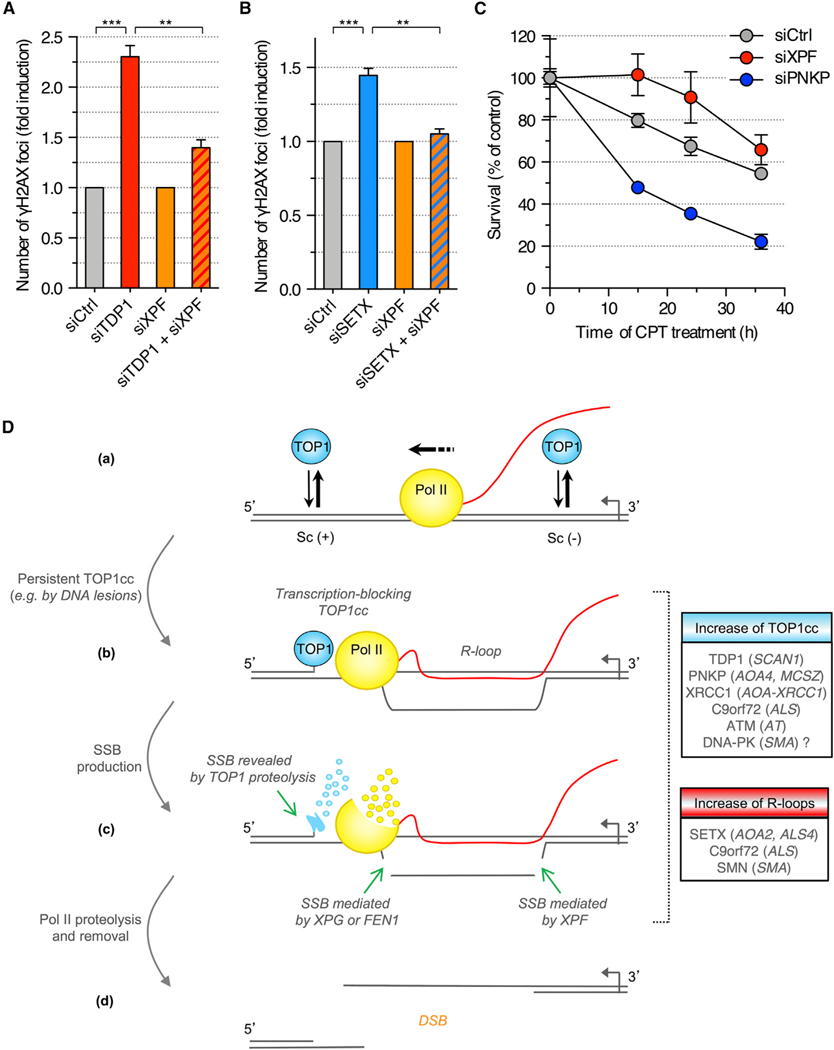
Figure 7. Depletion of XPF Prevents the Induction of DSBs upon Depletion of TDP1 in Quiescent Cells.
(A and B) Quiescent cells were transfected with the indicated siRNAs and co-stained for γH2AX and p53BP1. To compare XPF-proficient (siCtrl) and XPF-deficient (siXPF) cells upon depletion of TDP1 (A) or SETX (B), γH2AX induction was normalized to 1 in both siCtrl and siXPF cells (means ± SEM; n = 3). **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 (two-tailed unpaired t test).
(C) Viability of siRNA-transfected quiescent cells treated with 25 μM CPT (means ± SEM of triplicates).
(D) Model for the induction of DSBs during transcription. (a) TOP1 removes both positive and negative DNA supercoiling (Sc) generated during transcription. (b) Stabilization of a TOP1cc on the template strand blocks Pol II transcription and promotes R-loop formation. (c) The transcription-blocking TOP1cc is partially proteolyzed by the ubiquitin-proteasome system, which reveals the SSB. The R-loop is cleaved by a dual incision mediated by XPG and XPF or FEN1 and XPF (legend continued on next page) generating a SSB on the opposing DNA strand. Stalled Pol II is degraded and/or removed from the chromatin. (d) The two DNA strands separate forming a DSB. Boxes indicate human disorders associated with increase of TOP1cc (blue) or R-loop levels (red). Genes mutated in these disorders are indicated. ALS, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; AOA, ataxia with oculomotor apraxia; AT, ataxia telangiectasia; SCAN, spinocerebellar ataxia with axonal neuropathy; SMA, spinal muscular atrophy; SMN, survival motor neuron.
See also Figure S7.