Fig. 6.
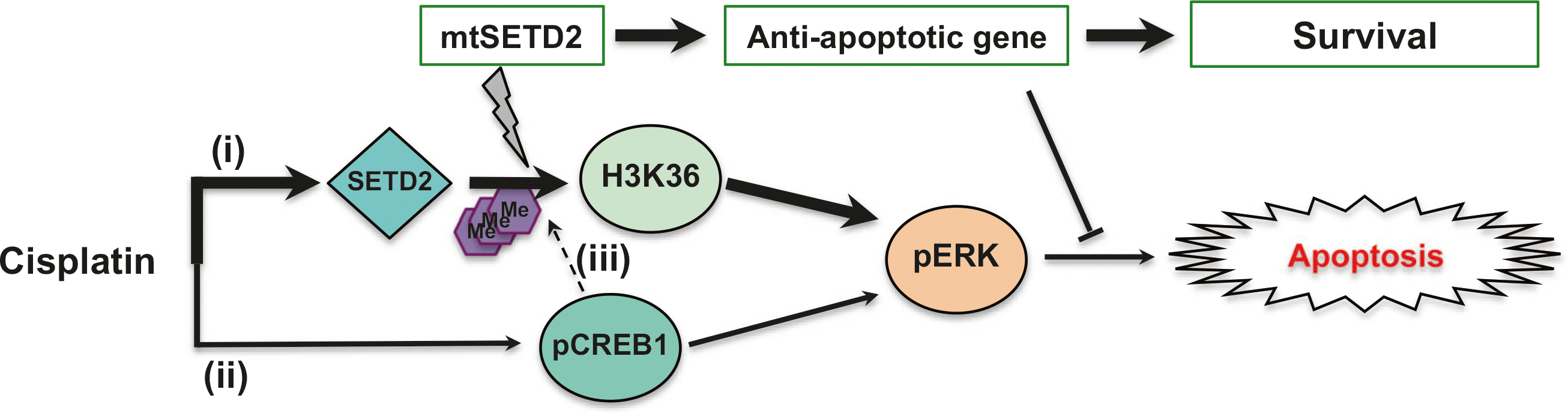
Proposed schematic representation of the role of SETD2 and CREB1 in the regulation of the cisplatin-induced apoptosis. Cisplatin induces cell death through SETD2-mediated trimethylation of H3K36 (H3K36me3) and ERK activation primarily (i) or CREB1 activation (ii). According to our results, resistance to cisplatin can occur through two different mechanisms, blockade of CREB1 activation or SETD2 mutation by epigenetic effectors inhibiting cisplatin-induced trimethylation H3K36 and ERK phosphorylation. Since CREB1 transactivates methyltransferase [48], CREB1 may play an important role in H3K36 methylation (iii). Me¸ methyl group
