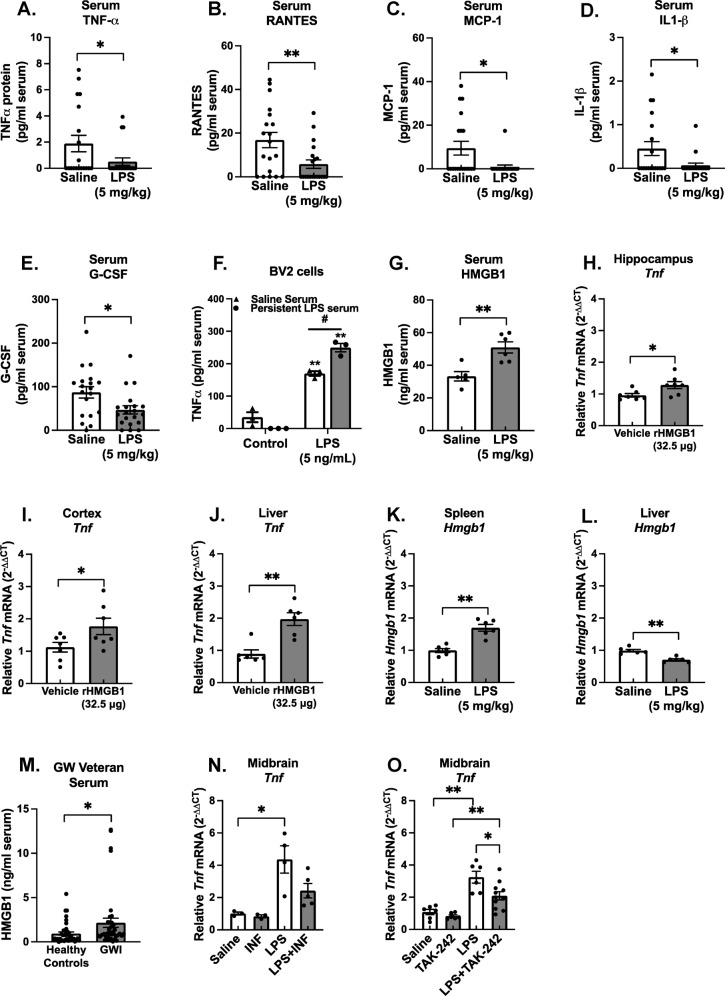
Fig. 2. The LPS PPM mouse model serum has ex vivo neuroimmune bioactivity, pro-inflammatory factors below baseline, and elevated HMGB1: implications for Gulf War Illness.
Male C57BL/6 mice received a single IP injection of LPS or saline and the serum was collected 7 days later in this model of Gulf War Illness- like persistent neuroinflammation. Protein levels of circulating traditional pro-inflammatory factors were determined in the serum using the Milliplex® multiplex assay and ELISA: (A) TNFα, (B) RANTES, (C) MCP-1, (D) IL1-β and (E) G-CSF, (G) HMGB1. (F) To assess neuroimmune bioactivity ex vivo, BV2 mouse microglia cells were treated with 2% serum obtained 7 days following LPS or saline injection with media alone or LPS (5 ng/ml), where the supernatant TNFα was measured 3 H later by ELISA. Data are reported as the mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 when compared to control and #p < 0.05 when compared between exposure groups (n = 5–20). Hmgb1 mRNA was assessed 7 days after LPS injection in the, (K) spleen Hmgb1 mRNA, and (L) liver. To determine if circulating HMGB1 could elicit neuroinflammation, C57BL/6 mice received a single tail vein injection of rHMGB1 or vehicle and Tnf mRNA expression was assessed 3 H later in the (H) hippocampus, (I) cortex, and (J) liver. mRNA levels were analyzed by qRT-PCR and normalized to Gapdh using the 2-ΔΔCT method. Data are reported as the mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 when compared to control (n = 3–7). (M) Serum samples from 40 veterans with Gulf War Illness (GWI) that had met the Kansas diagnostic for GWI and 40 healthy controls were assessed for levels of circulating HMGB1 by ELISA, Data are reported as the mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05 when compared to control (n = 40). To determine if HMGB1 inhibition could abolish the LPS-induced persistent neuroinflammation, at 24H after LPS injection, C57BL/6 mice were administered (N) Inflachromene (HMGB1 inhibitor,10 mg/kg) or vehicle IP or (O) TAK-242 (3 mg/kg, TLR4 inhibitor) or vehicle for 6 days and Tnf mRNA expression was assessed in the midbrain. Data are reported as the mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 when compared to control (n = 3–12).