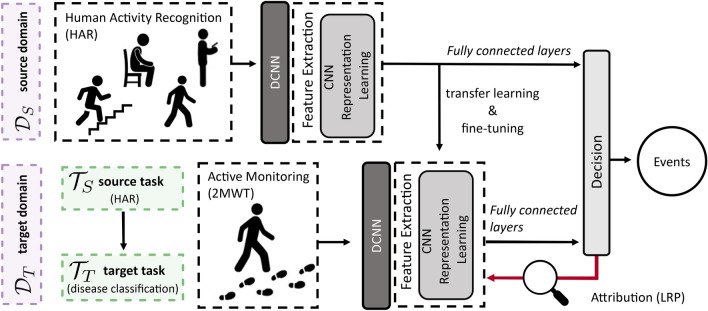
Figure 1.
Schematic of proposed smartphone-based remote disease classification approach. First, open-source datasets () were utilised to learn a HAR classification task () with a Deep Convolutional Neural Network (DCNN). Learned activity information was then subsequently transferred using the transfer learning (TL) framework, where a portion of the DCNN model is retrained on the FL datatset (), and parameters are fine-tuned towards the application of a disease recognition task (). DCNN model decisions can then be visually interpreted using attribution techniques, such as layer-wise relevance propagation (LRP), which aim to map the patterns of an input signal that are responsible for the activations within a network, and hence uncover pertinent MS disease-related ambulatory characteristics.