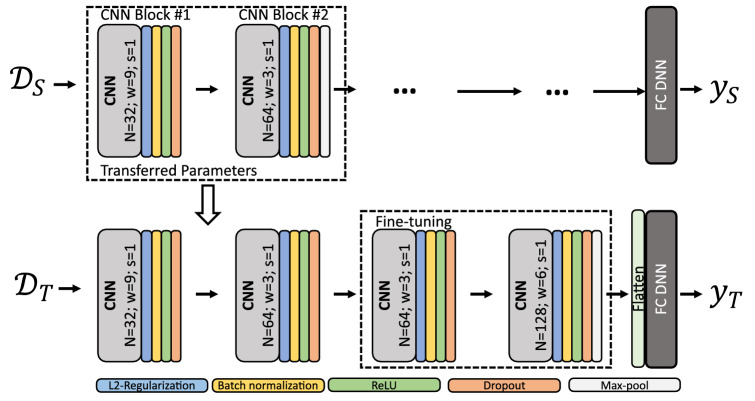
Figure 6.
Schematic of deep transfer learning approach. refers to input data from a source domain, in this case a HAR dataset, to learn a task , which is represented by the label space (the HAR activity classes). refers to the target domain, in this case the FLOODLIGHT data, where are the disease classification outputs of HC, PwMSmild or PwMSmod for target task . During transfer learning, a model’s parameters and learned weights, of , are then used to initialise and train a model on target domain and task . Transfer learning is then performed by transferring the source model’s layers (where these weights and parameters are “frozen”) to subsequently re-train a new model (i.e. fine-tune) using data for the new target task, . Downstream layers in the network are fine-tuned towards this new target task decision .