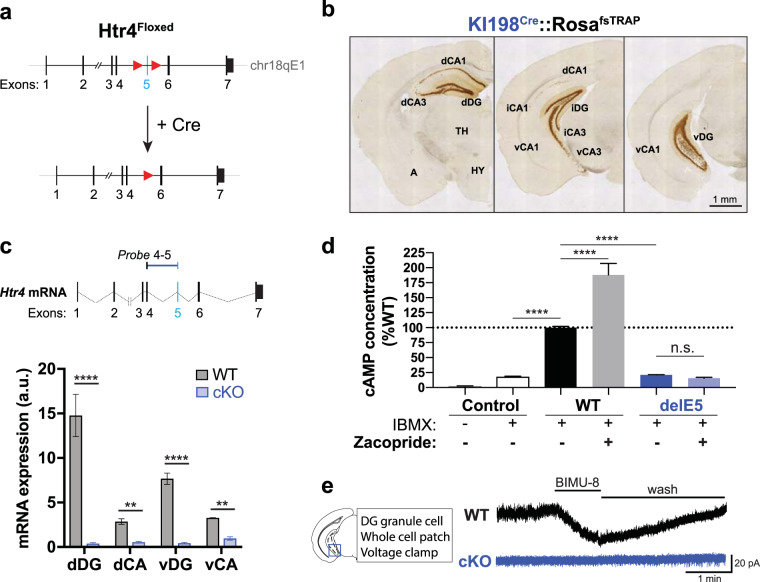
Fig. 1. Generation and validation of an Htr4Floxed mouse line.
a Schematic of Htr4Floxed allele. LoxP sites (red triangles) were inserted to flank Htr4 exon 5 (light blue bar) for Cre-mediated excision. b Low magnification anti-EGFP immunohistology of coronal brain sections from a KI198Cre::Rosa26fsTRAP mouse showing Cre expression in the hippocampus. dCA, iCA, vCA1/3: dorsal, intermediate, ventral CA1/3 fields, respectively; A: amygdala; TH: thalamus; HY: hypothalamus. c Schematic of the TaqMan probe spanning Htr4 exons 4 and 5 (Probe 4–5) is shown at top. Below, qRT-PCR (mean ± SEM) quantification showing diminished expression of Htr4 transcripts containing exon 5 along the dorsoventral axis of the hippocampus in Cre-negative (WT, gray) and cKO (blue) mice. Two-way ANOVA: genotype factor: F(1,24) = 439.0, p < 0.0001 followed by post hoc Fisher’s LSD test. n = 2–6 per group. d Quantification (mean ± SEM) of cAMP induction in HEK293T cells expressing EGFP (Control), intact 5-HT4R (WT), or Htr4delE5 (del5) in the presence or absence of the 5‑HT4R agonist, zacopride. One-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Fisher’s LSD test, n = 4 per group. e Representative traces of whole-cell voltage clamp recordings from DG GC in WT and cKO mice with bath administration of 10 mM BIMU-8. Scale bar: 1 min, 20 pA. Fisher’s LSD test, ****p < 0.0001, ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01, n.s. p > 0.05.