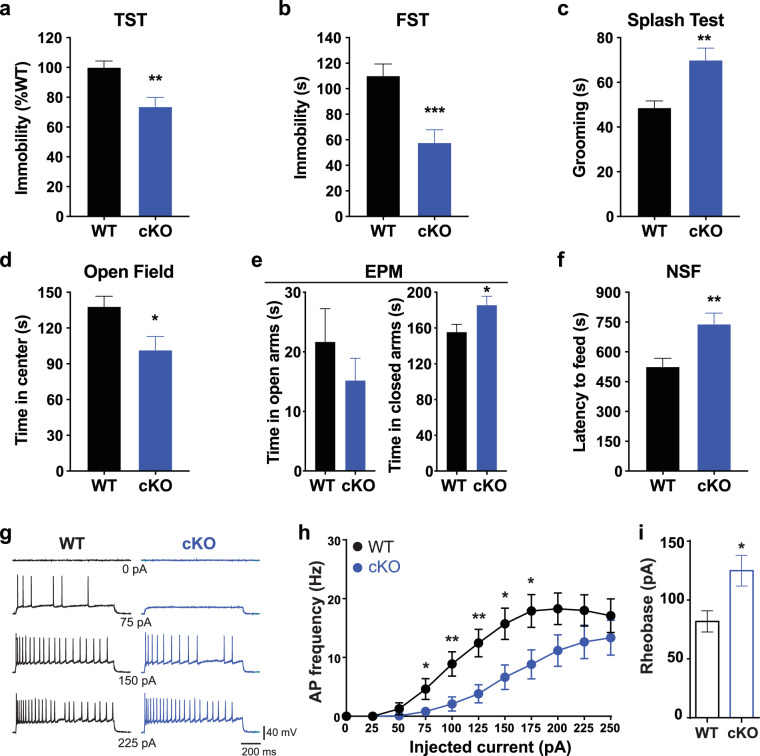
Fig. 3. cKO mice exhibit altered affective behaviors and reduced firing in vDG granule cells.
a Quantification of the time spent immobile in the tail suspension test (TST) in cKO mice (cKO, blue) and Cre-negative littermates (WT, black). **p = 0.0012, nWT = 19, ncKO = 16. b Quantification of the time spent immobile in the forced swim test (FST) for each genotype. ***p = 0.0005, nWT = 19, ncKO = 16. c Quantification of grooming time in the splash test for each genotype. **p = 0.001, nWT = 19, ncKO = 16. d Mean time spent in the center in the open field (OF) for each genotype. *p = 0.0139, nWT = 19, ncKO = 17. e Quantification of the time spent in the open (left) and closed (right) arms in the elevated plus maze (EPM). *p = 0.0239, nWT = 18, ncKO = 16. f Mean latency to feed in the novelty suppressed feeding (NSF) paradigm for each genotype. **p = 0.0033, nWT = 20, ncKO = 16. g Sample traces from whole-cell current-clamp recordings of GCs in hippocampal slices from WT and cKO mice showing spiking in response to different steps of injected current. h Quantification of the AP frequency of GCs in WT and cKO mice across current steps. i Histogram of rheobase measurements of GCs from WT and cKO mice. All data are represented as mean ± SEM and two-tailed unpaired t-tests were performed for all panels. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.