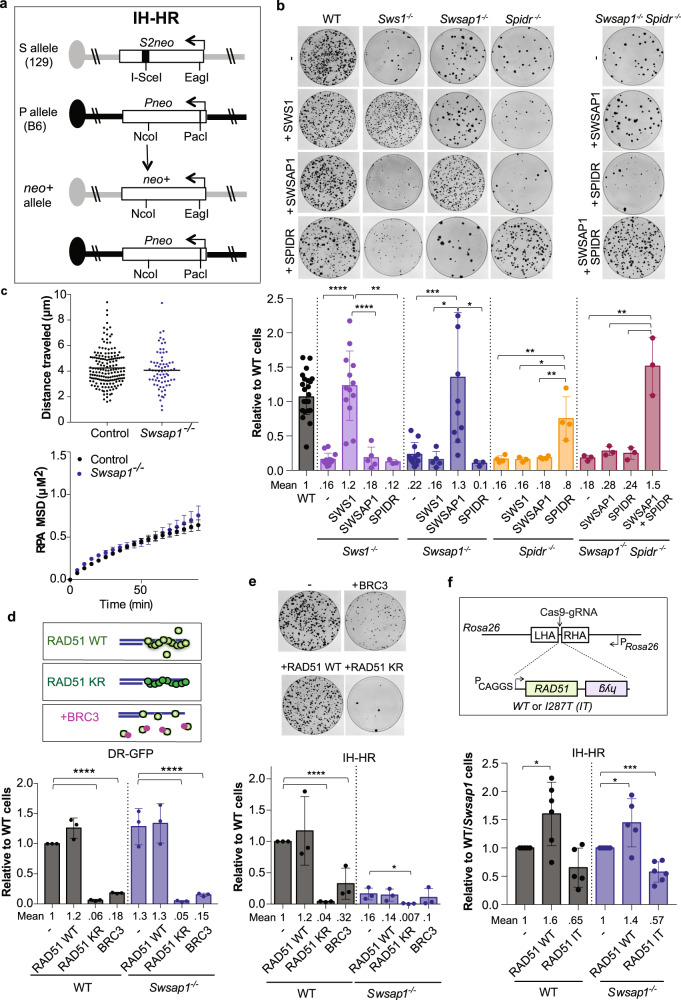
Fig. 2. The SWS1–SWSAP1–SPIDR complex promotes IH-HR.
a IH-HR at the S/P reporter in 129/B6 hybrid ES cells. The S allele on the 129 chromosome 14 contains the S2neo gene mutated by insertion of an I-SceI cleavage site at a NcoI restriction site, whereas the P allele on the B6 chromosome 14 contains the Pneo gene mutated by insertion of a PacI restriction site at an EagI site. After induction of an I-SceI-induced DSB in S2neo, IH-HR using the Pneo gene as a template results in a functional neomycin gene (neo+) that gives rise to G418 resistant colonies. b Sws1−/−, Swsap1−/−, Spidr−/−, and Swsap1−/− Spidr−/− cells show decreased numbers of neo+ colonies, indicative of reduced IH-HR, which is rescued by expression of the cognate proteins. Representative Giemsa-stained plates in S/P reporter cells after I-SceI expression are shown at the top with quantification below. Relative to WT cells, colony counts expressed relative to wild-type cells transfected with an empty vector within each experiment. WT n = 36, Sws1−/− n = 14, Sws1−/− +SWS1 n = 14, Sws1−/− +SWSAP1 n = 6, Sws1−/− +SPIDR n = 3, Swsap1−/− n = 12, Swsap1−/− +SWS1 n = 6, Swsap1−/− +SWSAP1 n = 12, Swsap1−/− +SPIDR n = 3, Spidr−/− n = 5, Spidr−/− +SWS1 n = 3, Spidr−/− +SWSAP1 n = 5, Spidr−/− +SPIDR n = 5, Swsap1−/−Spidr−/− n = 3, Swsap1−/−Spidr−/− +SWSAP1 n = 3, Swsap1−/−Spidr−/− +SPIDR n = 3, and Swsap1−/−Spidr−/− +SWSAP1 + SPIDR n = 3, where n is the number of independent experiments. (See also Supplementary Fig. 7a.). c DNA end mobility is not significantly altered by loss of SWSAP1. MEFs were treated with NCS (0.5 μg/mL) for 100 min and RPA-GFP foci (RPA32-GFP) were tracked. Top, the mean cumulative distance traveled by RPA-GFP foci in control and Swsap1-defective MEFs is similar. Bottom, The mean-square displacement (MSD) of RPA-GFP foci following NCS treatment is also similar: Control, 4.217 × 10−5 μm2 s−1; Swsap1−/−, 5.051 × 10−5 μm2 s−1. n = >450 foci in >8 cells. Error bars, weighted S.E.M. overall MSD curves. d, e RAD51 K133R (KR) and BRC3 peptide expression reduce HDR in both the DR-GFP (d) and IH-HR (e) reporters in wild-type cells. In Swsap1−/− cells, RAD51 K133R (KR) and BRC3 peptide expression reduces HDR in DR-GFP to a similar extent as in wild-type cells (d), whereas it further reduces IH-HR (e). RAD51 KR is overexpressed relative to endogenous RAD51 and forms filaments with slow turnover because of the ATP hydrolysis defect. BRC3 peptides can bind RAD51 and sequester it from forming nucleoprotein filaments. Relative to WT cells, % GFP+ or colony counts expressed relative to wild-type cells transfected with an empty vector within each experiment. For d, e, n = 3, where n is the number of independent experiments. f Constitutive overexpression of RAD51 WT increases IH-HR in wild-type and Swsap1−/− cells, whereas RAD51 I287T expression reduces IH-HR. WT n = 5, WT + RAD51 WT n = 6, WT + RAD51IT n = 5, Swsap1−/− n = 5, Swsap1−/− +RAD51 WT n = 5, Swsap1−/− +RAD51IT n = 6, where n is the number of independent experiments. An expression cassette for RAD51 WT or RAD51 I287T was targeted to Rosa26 locus81 in wild-type and Swsap1−/− cells, selecting for expression of the hyg gene from the Rosa26 promoter. Two targeted clones for each were analyzed in IH-HR assays. Relative to WT/Swsap1−/− cells, colony counts expressed relative to wild-type or Swsap1−/− cells (i.e., WT/Swsap1 cells on the y-axis) transfected with an empty vector (–) within each experiment. (See also Supplementary Fig. 7e, f) Error bars in b, d–f mean ± s.d. *P ≤ 0.05; **P ≤ 0.01; ***P ≤ 0.001; ****P ≤ 0.0001; unpaired t test, two-tailed. All source data are provided in the source data file.