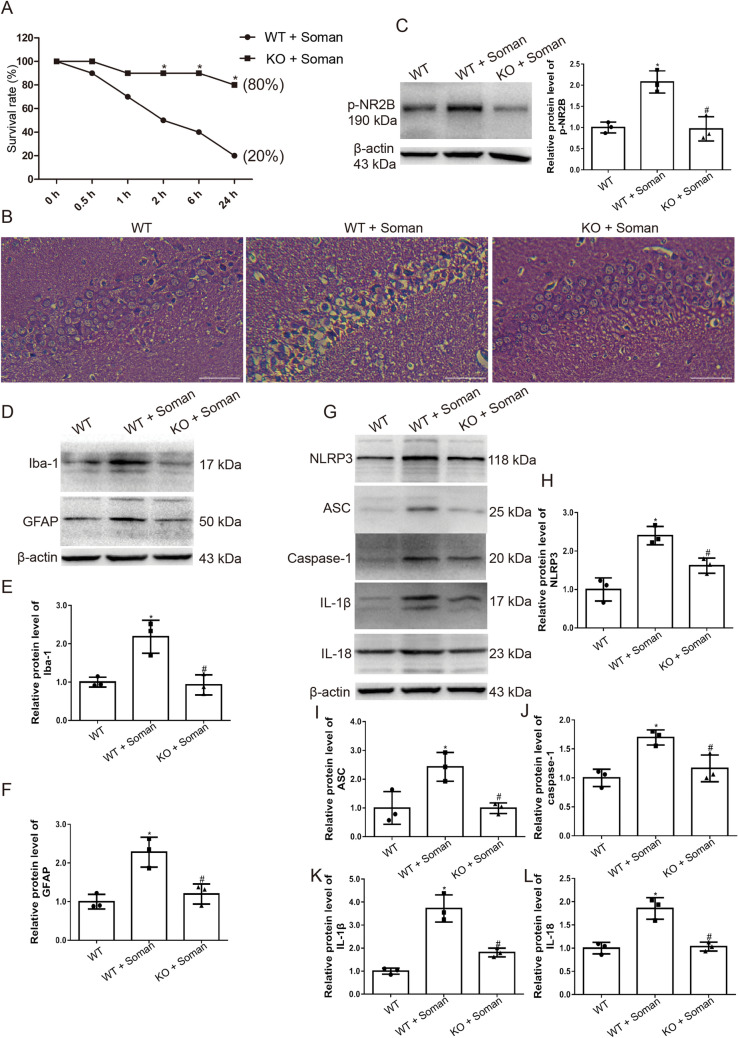
Fig. 8.
TRPV4-KO mice are protected against soman exposure. WT mice and TRPV4-KO mice were treated with HI-6 (125 mg/kg i.p.) before soman injection (125 μg/kg, s.c.). A Survival rates calculated as the number of living mice (24 h after soman exposure) divided by the total number of mice (n = 10; *P <0.05 vs WT + soman group. B Histological assessment showing severe injury, neuron loss, and nuclear pyknosis in the WT + soman group; TRPV4-KO reduces the histopathologic lesions in the hippocampus of mice caused by soman exposure (× 200, original magnification, scale bars, 50 μm). C TRPV4-KO inhibits NR2B phosphorylation in the hippocampus of mice exposed to soman, compared to the WT + soman group (mean ± SD, n = 3; *P <0.05 vs WT group, #P <0.05 vs WT + soman group. D, E Iba-1 reflects the activation state of microglial cells. Activation of astrocytes and microglial cells induced by soman is attenuated by TRPV4-KO (mean ± SD, n = 3; *P <0.05 vs WT group, #P <0.05 vs WT + soman group). D, F GFAP reflects the activation of astrocytes. Activation of astrocytes induced by soman is attenuated by TRPV4-KO (mean ± SD, n = 3; *P <0.05 vs WT group, #P <0.05 vs WT + soman group). G–L Western blots (G) and analysis of expression of the NLRP3 inflammasome complex proteins NLRP3 (H), ASC (I), caspase-1 (J), and downstream inflammatory cytokines IL-1β (K), IL-18 (L), and β-actin (mean ± SD, n = 3; *P <0.05 vs WT group, #P <0.05 vs WT + soman group, one-way ANOVA and Dunnett’s multiple comparison test).