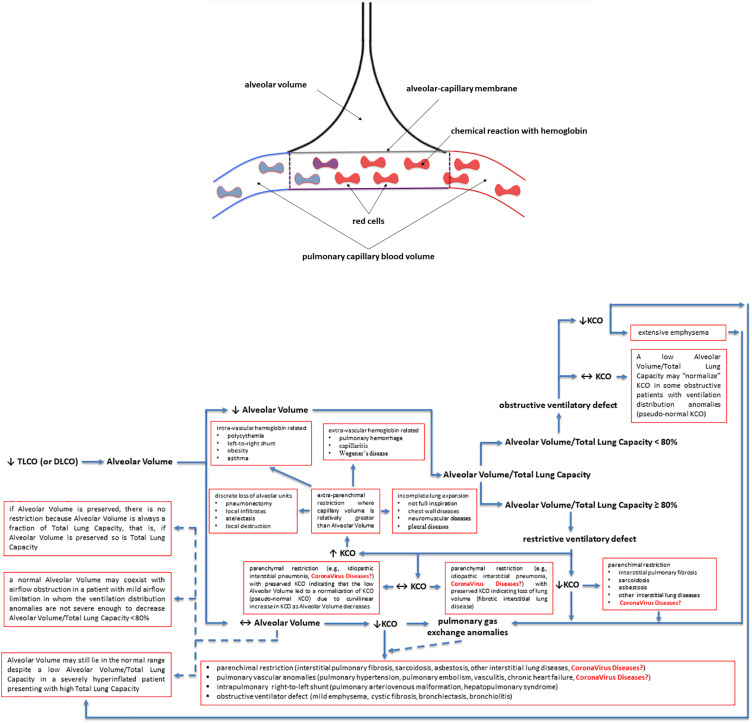
FIGURE 2.
Factors contributing to a decreased lung transfer (or diffusing) capacity for carbon monoxide (CO) (TLCO or DLCO) and the algorithm that allows physiologists and clinicians to unravel its mechanisms. If TLCO (or DLCO) is reduced, the next step is to check whether the Alveolar Volume is preserved or reduced. If Alveolar Volume is diminished, the next step is to check whether the Alveolar Volume/Total Lung Capacity ratio is low (<80%) due to ventilation maldistribution secondary to an obstructive ventilatory defect or is preserved (≥80%) due to restrictive ventilatory defect, associated or not with impaired pulmonary gas exchange. If Alveolar Volume is preserved, please follow the arrows in the algorithm to get some explanations and to see whether the KCO is reduced and there are pulmonary gas exchange anomalies associated with. KCO, transfer or diffusion coefficient (KCO = TLCO/Alveolar Volume or DLCO/Alveolar Volume); Coronavirus diseases is written in red as potential yet not fully understood mechanisms explaining the TLCO or DLCO anomalies observed in Coronavirus diseases, such as COVID-19 (caused by SARS-CoV-2), SARS (caused by SARS-CoV-1) and MERS (caused by MERS-CoV); SARS, Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome; MERS, Middle East Respiratory Syndrome; CoV, coronavirus; COVID-19, coronavirus disease 2019. See the text for more details and explanations. This is an original figure, no permission to reproduce is required.