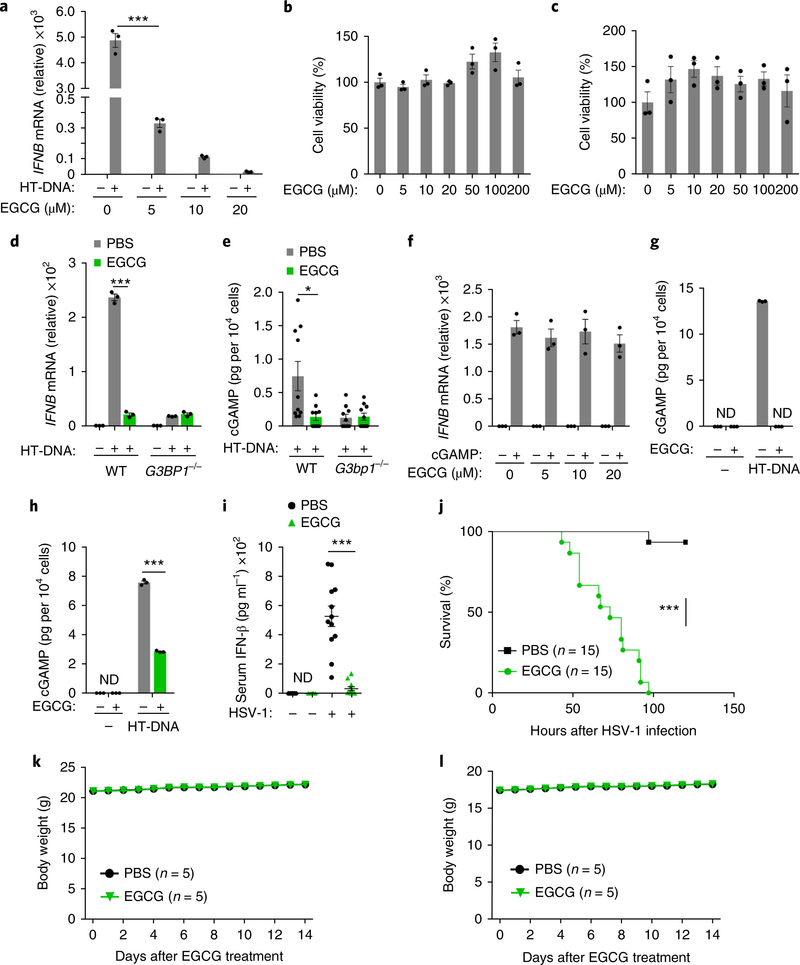
Fig. 6 |. EGCG blocks cGAS-mediated interferon production through inhibiting G3BP1.
a,f, qPCR analysis of IFNΒ mRNA expression in human primary macrophages treated with HT-DNA (0.5 μg ml−1) (a) or cGAMP (0.5 μg ml−1) (f) following a 1 hour of pretreatment with EGCG as indicated. b,c, MTS assay shows the cell viability of BMDMs (b) and human primary macrophages (c) incubated with EGCG at indicated concentrations for 48 h. d, The effect of EGCG on HT-DNA-induced IFNB production in U937 cells. e, The cGAMP production in MEFs transfected with HT-DNA following EGCG pretreatment. g,h, EGCG effect on HT-DNA-induced cGAMP production in human primary macrophages (g) and U937 cells (h) was analyzed by LC–MS/MRM, ND, non-detected. i, ELISA of serum IFN-β concentration of WT C57BL/6 mice injected with EGCG (40 mg kg−1) before infection with HSV-1 (1 × 107 pfu per mouse). Uninfected mice, n = 6. j, WT C57BL/6 mice (n = 15 per group) were pretreated with EGCG (40 mg kg−1, i.v.) for 12 h before infection with HSV-1 (i.v., 2 × 106 pfu per mouse). With continuous daily EGCG injection, the survival of mice was monitored for 120 h. k,l, Male (k) and female (l) WT C57BL/6 mice were treated with EGCG (120 mg kg−1) daily for 2 weeks. Body weight was measured every day. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001, two-tailed t-test (a,d,e,h,i), two-sided log-rank (Mantel–Cox) test (j). Data are representative of three experiments (a–d,f–h; mean ± s.e.m. of triplicate samples). Results are mean ± s.e.m. of n = 10 mice (e) or n = 12 mice (i) or n = 5 mice (k,l).