Figure 2.
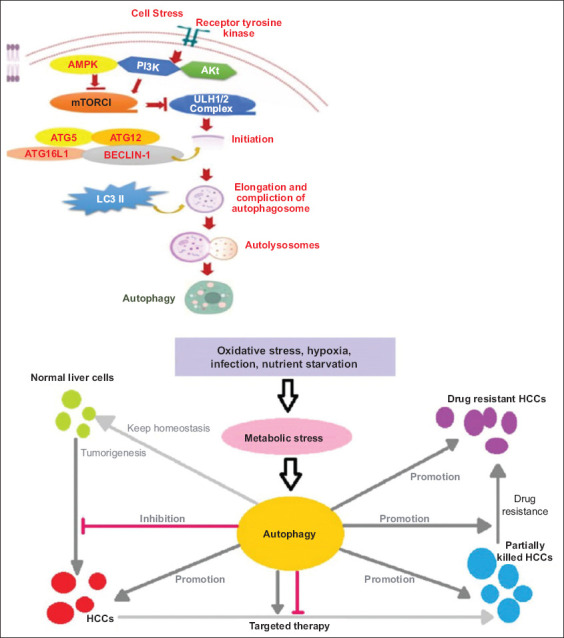
Autophagy reduction contributes to tumor initiation, and increased autophagy allows cancer cells to survive under stress conditions. The function of autophagy in liver cancer is a topic of concern, and it plays multiple roles in different situations. In normal liver cells, basal autophagy is involved in maintaining liver homeostasis. Once hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is established, autophagy plays a promotional role in tumor development, metastasis, and therapeutic resistance. Thus, appropriate autophagy inhibition could effectively suppress HCC growth and metastasis. However, in targeted HCC therapy, the role of autophagy is uncertain, for either inhibition or promotion, according to the different characteristics of agents. Autophagy induction at the tumor development stage promotes resistance to cancer therapy, while inhibition of autophagy promotes cancer cell death during cancer therapy
