Figure 5. Mechanisms of action of bacterial glycosylation inhibitors and representative structures of each class of inhibitors.
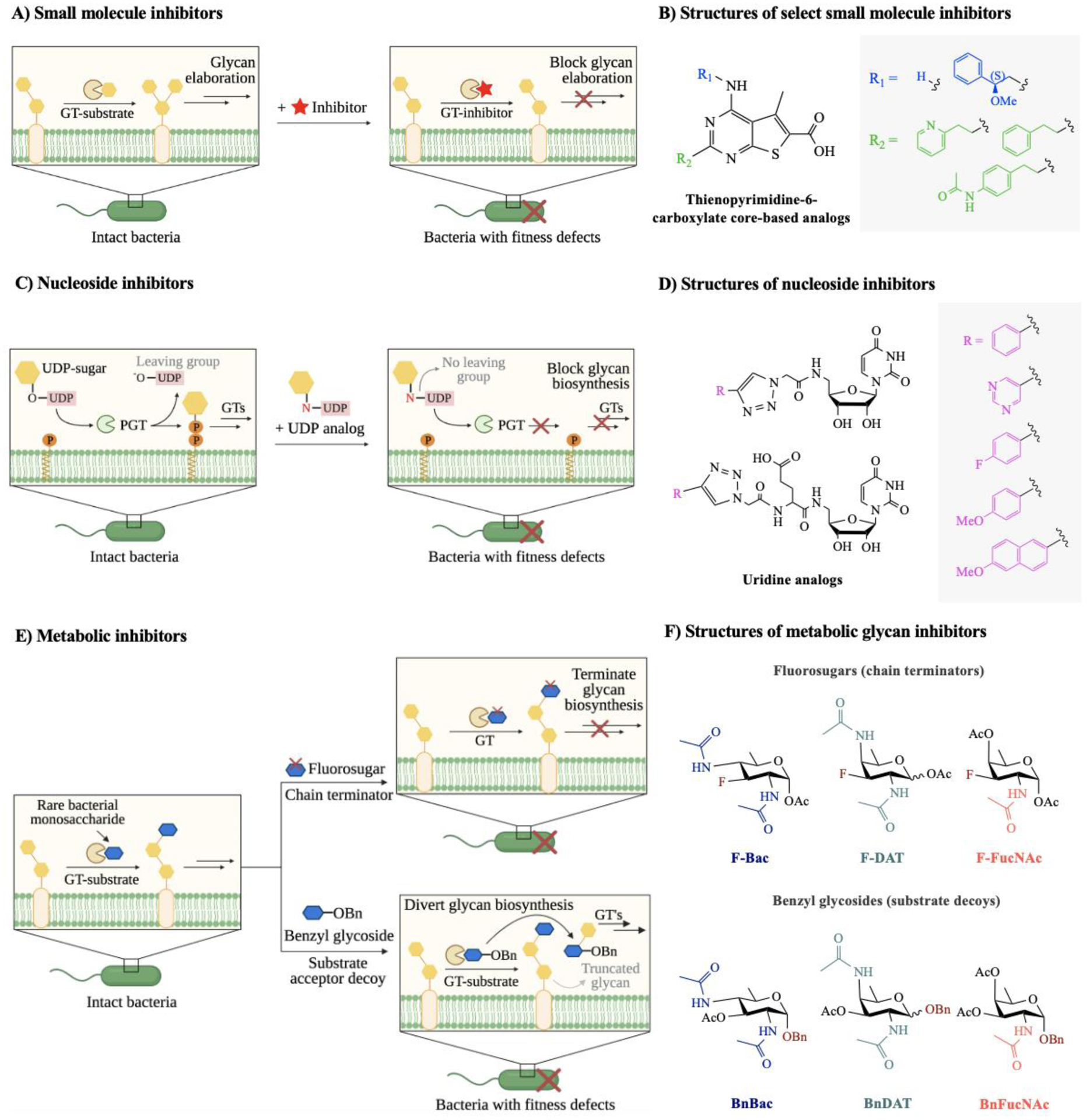
A) Small molecule inhibitors compete with natural substrates in the active site of the target glycosyltransferase (GT), leading to the reduction of glycan production in the associated glycan biosynthetic pathway. B) Structures of representative small molecule inhibitors accessed from thienopyrimidine-6-carboxylate core-based analogs.113 C) Phosphoglycosyl transferases (PGTs) initiate glycan biosynthesis on a lipid carrier by catalyzing the transfer of a nucleoside sugar to a polyprenyl phosphate. Uridine analogs inhibit PGT activity and block addition of monosaccharides onto the lipid carrier. D) Structures of representative nucleoside inhibitors accessed from uridine analogs.115 E) Metabolic inhibitors consist of two classes: fluorosugars (chain terminators) and benzyl glycosides (substrate decoys). Fluorosugars terminate glycan elongation, while benzyl glycosides mimic endogenous glycan acceptors and divert glycan biosynthesis onto decoy substrates. F) Structures of representative metabolic inhibitors accessed from rare deoxy amino sugars, featuring chain terminators and substrate decoys.53 Abbreviations: Bac = bacillosamine (blue hexagon); DAT = 2,4-diacetamido-2,4,6-trideoxygalactose; FucNAc = N-acetylfucosamine.
