Figure 6. Blocking glycan binding events key to pathogenesis.
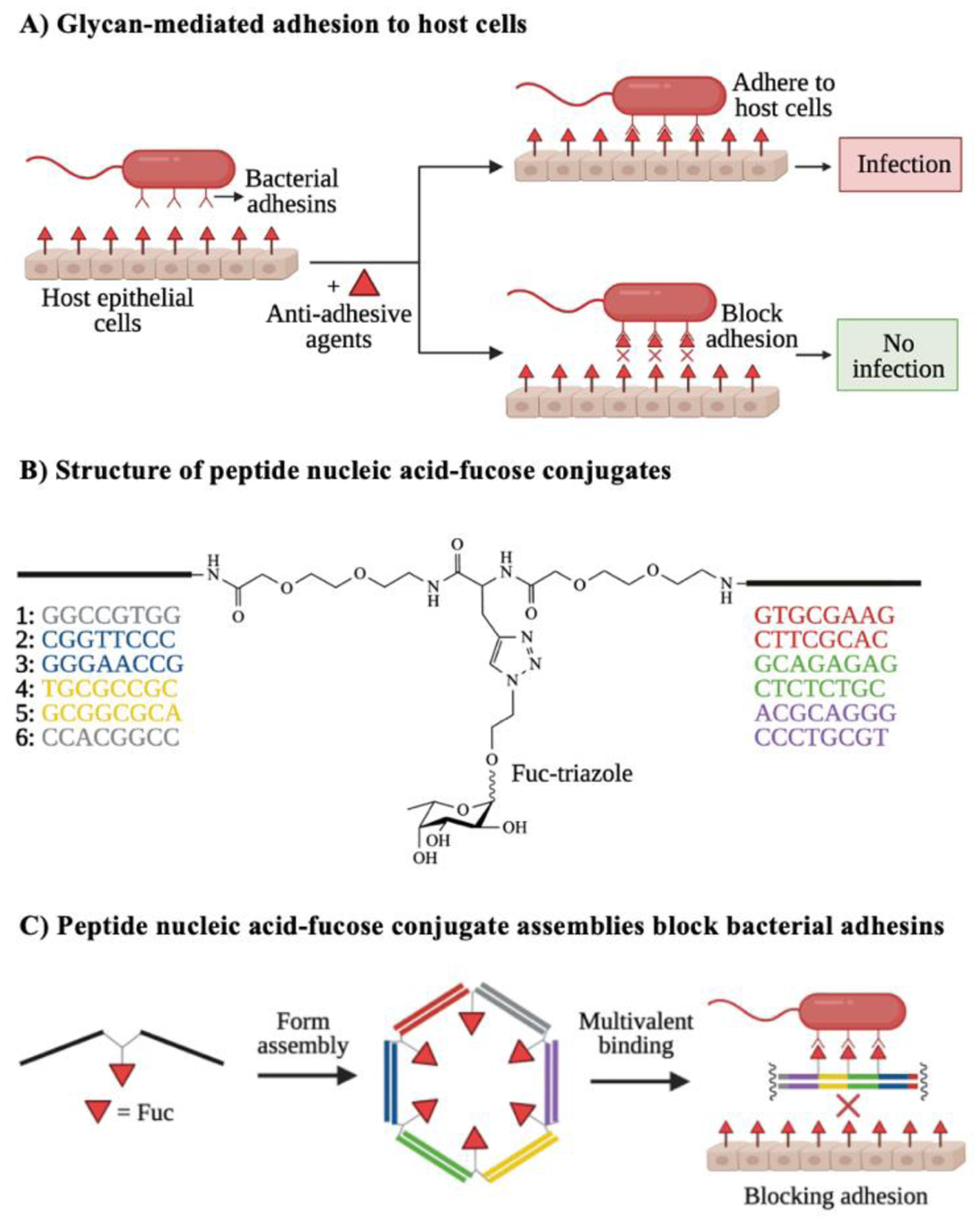
A) Bacterial adhesion to host cells often depends on host-pathogen interactions. Anti-adhesive agents that bind to either bacterial adhesins or host receptors can block these glycan-mediated binding events, resulting in reduced infection. B) Structure of representative synthetic anti-adhesive compounds, featuring peptide nucleic acid-fucose conjugates. C) Peptide nucleic acid-fucose conjugates can form assemblies that bind to bacterial adhesins in a multivalent fashion and block bacterial entry to the host. Images B and C are inspired by Figure 2 from Machida et al.117
