Figure 7|. Models of transposition mechanisms of CAST I-B and CAST V-K systems.
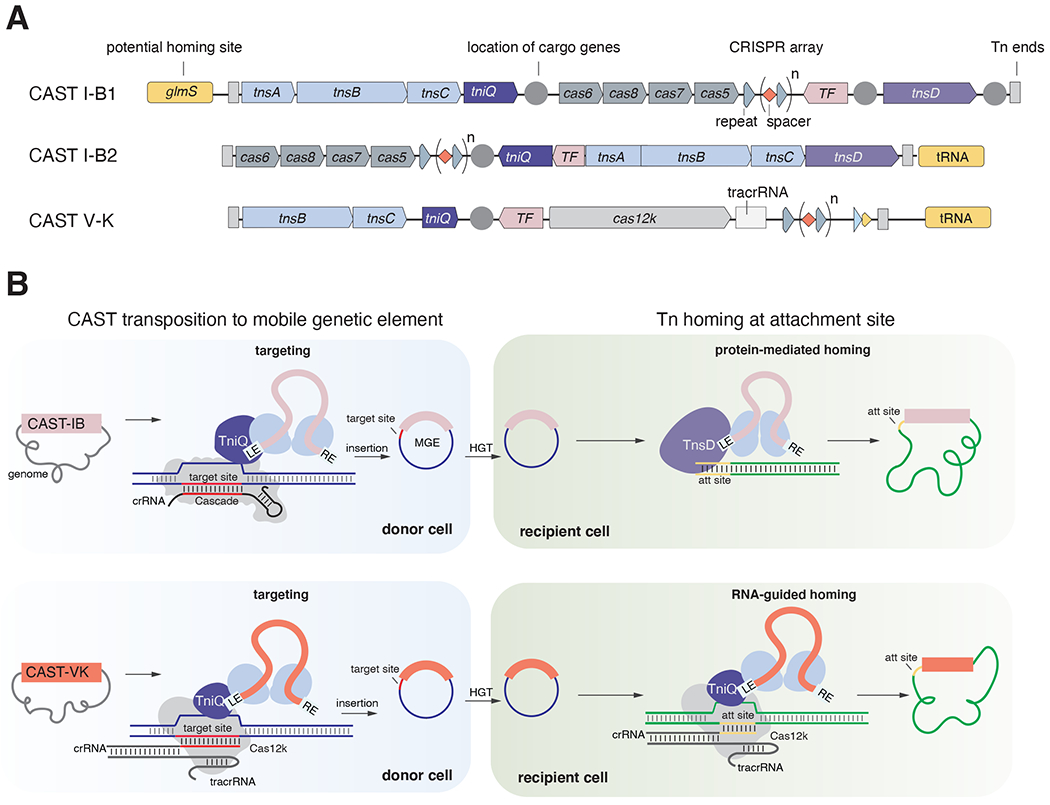
(A) Prototypical loci organization of CAST I-B and CAST V-K systems. The loci are delimited by transposon ends (Tn ends, indicated as light vertical rectangle). Transposon core components (tnsA, tnsB, and tnsC in CAST I-B; tnsB and tnsC in CAST V-K) are colored in light blue while tniQ are indicated in purple with a lighter purple for tnsD. Cas components (Cascade and cas12k) are shown in grey. Conserved transcription factors (TF) are shown in pink. Locations of cargo genes are indicated with dark grey circles. CRISPR arrays are shown as grey triangles for the repeats and red diamonds for the spacers. The delocalized crRNA is indicated by a lighter triangle (partial repeat) and a truncated red diamond (short spacer). Homing target sites are colored in yellow. Horizontal light grey triangle indicates the tracrRNA in the CAST V-K locus. Conserved transcription factors (TF) are shown in light pink. (B) Models for CAST transposition to mobile element (donor cell in blue) and CAST homing transposition to bacterial chromosome (recipient cell in green). CAST transposition to mobile genetic elements is mediated by the Cas effector machinery (IB Cascade and crRNA or Cas12k, tracrRNA, and cRNA; Cas proteins are shown in grey) that recognizes the target site (red) with RNA-guided targeting to insert the transposon using Tn components. TniQ may function as an adaptor between Cas machinery and the transpososome (Tn core machinery bound to the DNA transposon). The mobile genetic element (MGE) where the transposon has inserted can be horizontally transferred (via HGT) to another host where homing transposition can occur. CAST I-B homing transposition is mediated by TnsD (without Cas components), which targets the homing site (light orange) located in the bacterial chromosome (in green). CAST V-K uses a dedicated crRNA to target the homing site.
