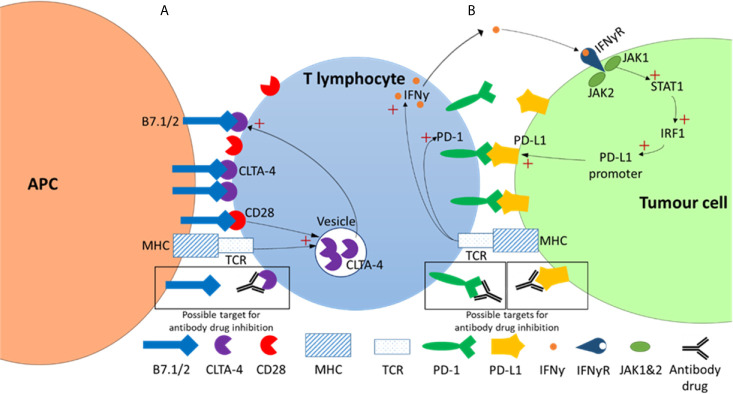
Figure 2.
CTLA-4 and PD-1 checkpoint inhibitor pathways. (A) CTLA-4 pathway. In this pathway strong TCR-HMC and CD28-B7 binding signals initiate the exocytosis of the CTLA-4 from the intracellular vesicles to the T cell surface. As CLTA-4 has a higher binding affinity then CD28 for B7, this results in a net negative signal that results in reduced T cell proliferation, survival and a decrease in growth cytokines such as IL-2. (B) In the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway TCR-HMC signalling up regulates both PD-1 and interferon-γ (IFNƴ) expression. The increased of IFNƴ in the tumor microenvironment activates the signalling pathway of Janus kinase (JAK)/signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) which activates the transcription factor interferon regulatory factor 1 (IRF1), which in turn induces PD-L1 expression. PD-1/PD-L1 interaction results in in a net negative signal and ultimately reduced T cell survival, proliferation and cytotoxic production. Possible antibody drug targets in both pathways are indicated showing antibody-target interaction (within black boxes).