Figure 3.
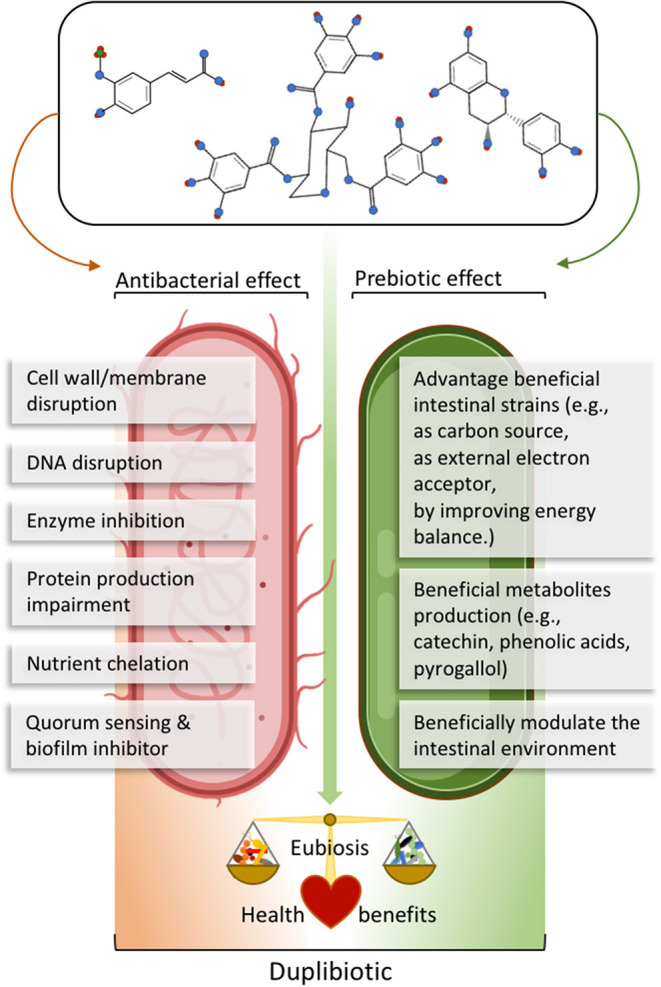
Description of (poly)phenols direct antibacterial and prebiotic effects. The antibacterial effect corresponds to the direct detrimental interaction between (poly)phenols or their metabolites and bacteria, while the prebiotic effect corresponds to the beneficial effect generated through direct bacterial metabolic utilization of (poly)phenols or their metabolites. The term duplibiotic design a non-digestible compound that, once reaching the colon, interacts with the gut microbiota through a dual antibacterial and prebiotic effect, favoring a eubiotic intestinal state and providing health benefits to the host.
