Figure 4.
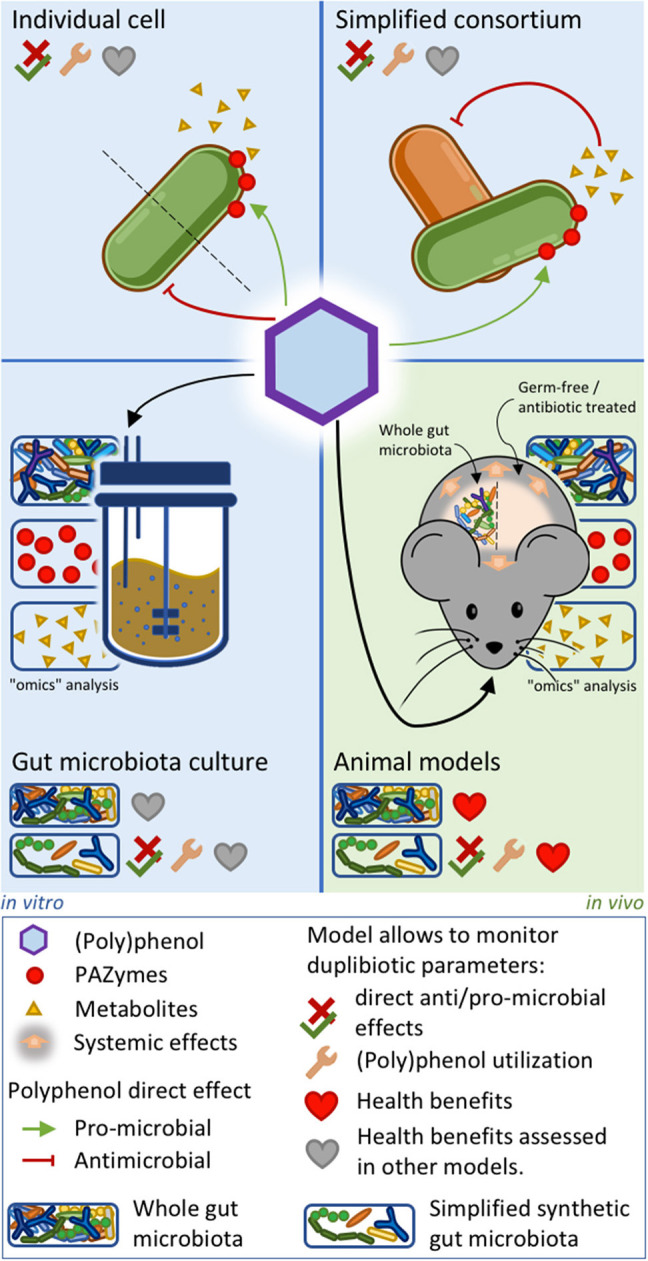
In vitro and animal approaches to evaluate duplibiotic nature of polyphenols. Individual bacterial strain or simplified bacterial consortium models allow determining (poly)phenol anti/pro-microbial effects, (poly)phenol transformation, and metabolite production. In addition, studies on simplified bacterial consortia can characterize symbiotic interactions. Gut microbiota culture and animal models combined with omics approaches provide insights on global microbial changes induced by (poly)phenols. Studies on conventionally grown, gnotobiotic, and antibiotic-treated animal models allow characterizing host health benefits. The health benefits stemming from the three in vitro approaches can be further demonstrated by transferring downstream metabolites into ex vivo systems. Synthetic microbiota inoculated in culture systems or in germ-free animals allows determining direct anti/pro-microbial effects, as well as demonstrating bacterial (poly)phenol utilization.
