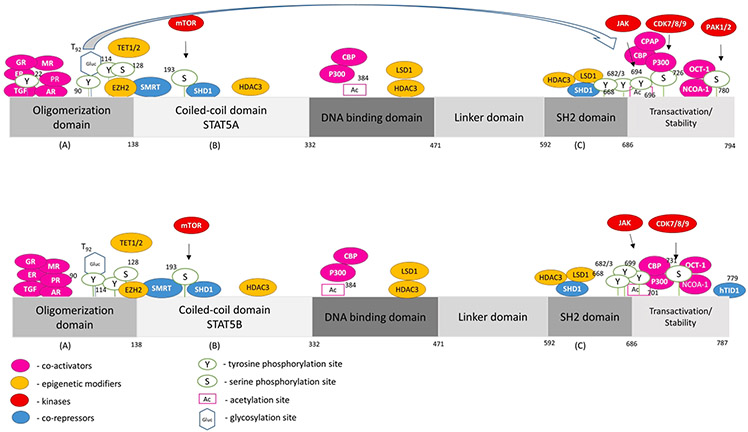
Fig. 2. STAT5A and STAT5B interactome and mutational landscape.
Human STAT5A and STAT5B contain 794 and 787 amino acids, respectively. The proteins consist of an oligomerization domain, a coiled-coil domain, a DNA binding domain, a linker domain, an SH2 domain and a transactivation domain. Three different dimerization domains (A, B, C) allow versatile complex formations of STAT5A/B proteins. We depict proteins physically interacting with STAT5A/B (co-activators, epigenetic modifiers, kinases and co-repressors, shown in colors as indicated), as well as post-translational modifications, with black arrows linking the proteins with their respective post-translational modification above each STAT5 schematic protein structure. The data of post-translational modifications were collected from PhosphoSitePlus® and selected due to biological importance in current literature insight. More precisely, we show acetylation sites reported in HTP (high-throughput papers), phosphorylation reported in more than 5 HTP or 10 LTP (low-throughput papers), and glycosylation [29]. The term “high-throughput papers” refers to records in which a certain modification was assigned using only proteomic discovery mass spectrometry, while the term “low-throughput papers” refers to records which assigned the certain modification using methods other than proteomic mass spectrometry.