Figure 12.
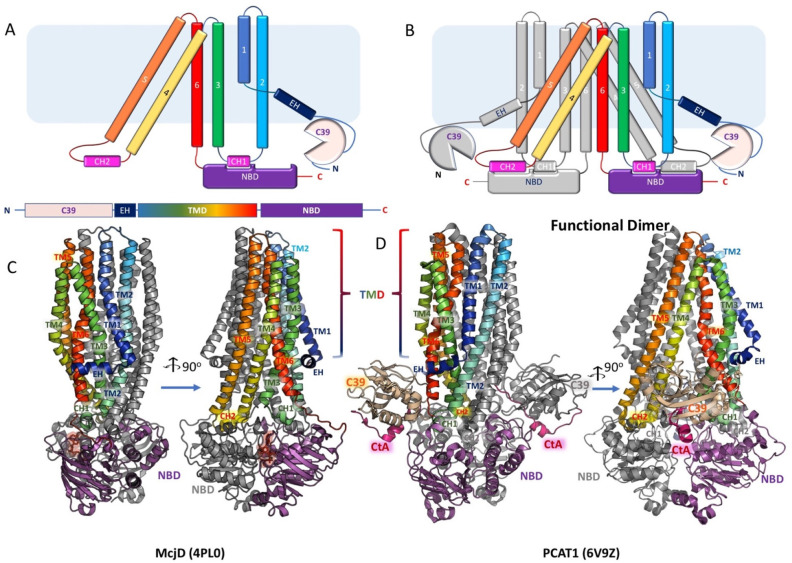
General view of the type IV ABC transporter topology and features of the typical type IV ABC transporter structure. Schematic representation of the topology of the isolated monomer of ABC transporters belonging to the type IV group (panel A) and the dimeric formation (panel B), highlighting the cross-protomer engagement of the nucleotide binding domains (NBDs) by the coupling helices 1 and 2 (CH1 and CH2, respectively). The optional N-terminal C39 or C39-like domain (CLD), which is present in a subset of the family, is shown as a “packman”. The TMD is presented as a rainbow from N- to C-terminal, and the EH represents the elbow helix. The second protomer of HlyB is presented in gray. Approximate membrane boundaries are represented by the blue rectangle. (C) View of a microcin-transport associated McjD based on the PDB ID 4PL0 (two side views 90° apart) highlighting the principal structural elements. Coloring as in panels A and B. (D) PCAT1 in complex with its transported peptide CtA, based on the PDB ID 6 V9Z. The C39-domain is colored wheat.