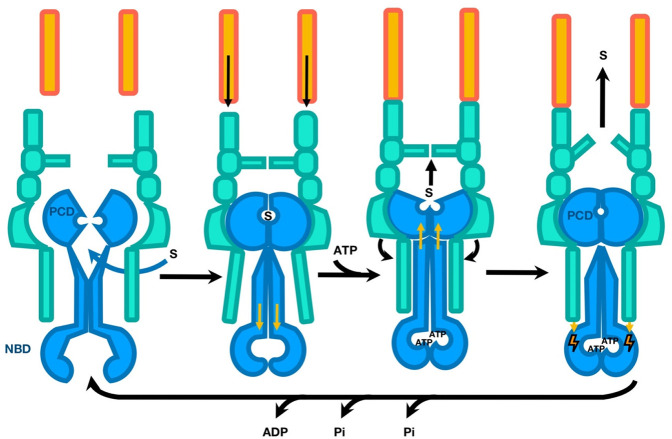
Figure 52.
Modified molecular bellows mechanism for the MacAB-TolC pump. MacA (green-cyan) and MacB (blue) undergo allosteric conformational transitions (symbolized by orange arrows) upon binding of substrate and ATP. Similar to type IV ABC transporters, substrate binding is suggested to bring a conformational transition that enables the nucleotide bidning domains (NBDs) to engage with ATP. Substrate is expelled through TolC (orange) upon ATP binding. ATP-hydrolysis (symbolized by the small orange lightning bolts) resets the pump, in order for another cycle of efflux to proceed. Interactions within the membrane between the TM-domains of the MacA and MacB are suggested to provide an additional level of transmembrane communication. See text for further details.